Ashar Prayoga
Introduction
Assalamualaikum wr. wb. Perkenalkan nama saya Ashar Prayoga, saya adalah mahasiswa program studi Teknik Mesin angkatan 2021 dengan NPM 2106727954. Di laman ini saya akan membagikan tentang hasil pembelajaran saya untuk kelas Metode Numerik-01, harapannya semoga apa yang saya tulis disini dapat bermanfaat di kemudian hari.
Contents
Framework DAI5
DAI5 adalah sebuah framework problem-solving yang dirancang untuk membantu seseorang melakukan pendekatan secara sadar dalam memecahkan masalah. Framework ini menggabungkan unsur brainware dan heartware, yang mana keduanya saling melengkapi dalam proses berpikir. Brainware mewakili aspek rasional dan logis, sementara heartware mewakili aspek emosional dan intuitif, sehingga solusi yang dihasilkan lebih holistik.
Tahapan Framework DAI5
1. Intention: Setelah masalah dikenali, tahap selanjutnya adalah menentukan intention atau niat. Niat ini penting karena akan menjadi landasan dari semua keputusan dan tindakan yang diambil selanjutnya. Pada tahap ini, seseorang perlu mempertanyakan tujuan dari pemecahan masalah tersebut dan memastikan bahwa tujuannya jelas serta selaras dengan nilai-nilai pribadi.
2. Initial Thinking: Tahap ini adalah proses eksplorasi awal ide dan solusi yang mungkin. Dengan menggunakan unsur brainware, seseorang akan mulai menyusun strategi atau kemungkinan solusi berdasarkan data dan fakta yang ada. Heartware juga berperan untuk memastikan ide-ide tersebut tetap terhubung dengan tujuan yang ingin dicapai dan mempertimbangkan faktor-faktor emosional yang mungkin mempengaruhi solusi.
3. Idealization: Di tahap ini, solusi terbaik dibayangkan atau di-idealize. Individu atau tim yang menggunakan metode DAI5 akan menggambarkan hasil ideal dari solusi tersebut, termasuk dampak positif yang diharapkan. Tahap ini berfungsi sebagai visualisasi tujuan akhir yang diinginkan, memberikan motivasi serta arah dalam penerapan solusi.
4. Instruction Set: Setelah solusi ideal dipahami, langkah terakhir adalah membuat instruction set atau rencana implementasi yang terperinci. Instruksi ini berupa langkah-langkah konkret yang perlu diambil untuk mencapai hasil yang diinginkan. Setiap langkah diatur dengan jelas agar proses implementasi dapat berjalan secara efektif dan efisien.
Framework DAI5 menekankan pada kesadaran penuh di setiap tahapan untuk mencapai solusi yang benar-benar menyeluruh dan berdampak positif.
Solving a 1D Finite Element Method using DAI5 Framework
Question: solve this problem using DAI5 framework
Answer:
Question: can you provide with algorithm, flow chart and python code
Answer:
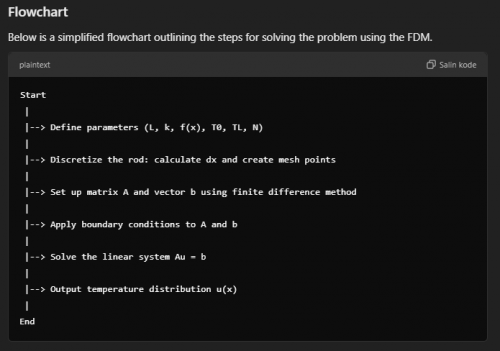
Algorithm
Flowchart
Python Code
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Define parameters
L = 10.0 # Length of the rod
N = 100 # Number of divisions (number of interior points)
k = 1.0 # Thermal conductivity
T0 = 100.0 # Temperature at the left end (boundary condition)
TL = 200.0 # Temperature at the right end (boundary condition)
# Define heat source function (can be constant or variable)
def f(x):
return 5.0 # Constant heat source; change this function if f(x) varies
# Discretize the rod
dx = L / (N + 1) # Calculate spacing
x = np.linspace(0, L, N + 2) # Generate x values including boundary points
# Initialize matrix A and vector b
A = np.zeros((N, N))
b = np.zeros(N)
# Fill in A and b based on finite difference method
for i in range(N):
if i > 0:
A[i, i - 1] = 1
A[i, i] = -2
if i < N - 1:
A[i, i + 1] = 1
b[i] = -f(x[i + 1]) * dx**2 / k # Adjust index for interior points
# Apply boundary conditions to b
b[0] -= T0
b[-1] -= TL
# Solve the linear system
u_interior = np.linalg.solve(A, b)
# Append boundary conditions to solution
u = np.zeros(N + 2)
u[0] = T0
u[1:-1] = u_interior
u[-1] = TL
# Plot the temperature distribution
plt.plot(x, u, label="Temperature Distribution")
plt.xlabel("Position along the rod (x)")
plt.ylabel("Temperature (u)")
plt.title("Steady State Temperature Distribution in 1D Rod")
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Design and Optimization of Pressurized Hydrogen Storage
When designing the optimization of pressurized hydrogen storage with a volume of 1 liter, pressure of 8 bar, and a production cost not exceeding Rp500,000.00, there are several considerations to take into account. Here are some important factors to consider:
1. Container Material and Construction
- Choose materials that are safe and resistant to high pressure and corrosion, such as aluminum, stainless steel, or carbon fiber-reinforced composites.
- Ensure that the container construction can safely withstand the desired hydrogen pressure.
2. Safety
- Certification and compliance with applicable safety standards such as ISO 15869 or SAE J2579.
- Consider adequate safety features, such as pressure relief valves, pressure sensors, and fire suppression systems.
3. Space Efficiency
- Design the container to maximize the use of space within the 1-liter volume.
- Utilize optimal packaging techniques to maximize the amount of hydrogen that can be stored within the available space.
4. Storage Efficiency
- Consider the most efficient method of hydrogen storage, such as physical storage as compressed gas or storage in the form of a fuel cell if hydrogen fuel cells are being :considered.
5. Production Cost
- Take into account the cost of materials, production, and testing associated with the storage design.
- Optimize the design to achieve a production cost that does not exceed the budgetary constraints.
6. Reliability
- Ensure that the container design can maintain a stable pressure over the desired period without leaks or potential damage.
7. Regulations
- Ensure that the design complies with applicable regulations and standards in the hydrogen storage industry.
Design Calculation
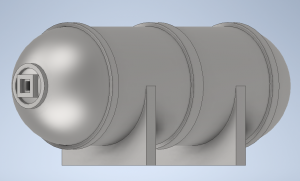
Specification of a Cylindrical Hydrogen Tank
Capacity : 1 liter Pressure : 8 bar Material : ASTM A36 sheet metal Cost : Rp500.000,00
Code to Optimize The Design of Cylindrical Hydrogen Tank
To optimize the design, i write a code in Python to find the optimium thickness, radius, and the height of the tank with cost and volume as a constant variables. Here is the code that i used:
from scipy.optimize import minimize
def objective_function(x):
thickness, radius, height = x[0], x[1], x[2]
# Calculate the weight of the tank (assuming density of ASTM A36 sheet metal)
density_astm_a36 = 7850 # kg/m^3 (density of ASTM A36 sheet metal)
volume = 3.14159 * radius * radius * height / 1000 # Convert to liters
weight = density_astm_a36 * volume
# Calculate the cost of the tank (based on material price per kg)
material_price = 500000 / weight # Rp/kg (maximum allowed cost divided by weight)
cost = weight * material_price
# Define the objective function as a combination of weight and cost
# You can adjust the coefficients based on your preference for weight vs. cost
objective_value = weight + 0.001 * cost
return objective_value
def constraint(x):
thickness, radius, height = x[0], x[1], x[2]
# Volume constraint: tank volume should be 1 liter
volume = 3.14159 * radius * radius * height / 1000 # Convert to liters
# Pressure constraint: tank should handle 8 bar pressure with a safety factor of 2
allowable_stress = 250e6 # Pa (allowable stress for ASTM A36 sheet metal)
inside_radius = radius - thickness # Inner radius of the tank
pressure = 8e5 # Pa (8 bar pressure)
stress = pressure * inside_radius / thickness # Stress in the tank wall
safety_factor = 2.0 # Safety factor
stress_allowable = allowable_stress / safety_factor
return [
volume - 1, # Volume constraint (1 liter)
stress - stress_allowable, # Pressure constraint
thickness - 5, # Minimum thickness constraint (5 mm)
10 - thickness # Maximum thickness constraint (10 mm)
]
# Initial guess for thickness, radius, and height (in mm)
x0 = [10.0, 50.0, 100.0]
# Define bounds for thickness, radius, and height (in mm)
bounds = [
(5, 10), # Bounds for thickness (assumed range from 5 to 10 mm)
(1, 50), # Bounds for radius (assumed range from 1 to 50 mm)
(100, 1000) # Bounds for height (assumed range from 100 to 1000 mm)
]
# Define the optimization problem
problem = {
'type': 'SLSQP',
'fun': objective_function,
'x0': x0,
'bounds': bounds,
'constraints': [{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': lambda x: constraint(x)}]
}
# Solve the optimization problem
result = minimize(problem['fun'], x0=problem['x0'], bounds=problem['bounds'], constraints=problem['constraints'], method=problem['type'])
# Extract the optimal solution
optimal_thickness, optimal_radius, optimal_height = result.x
# Calculate the weight of the tank (assuming density of ASTM A36 sheet metal)
density_astm_a36 = 7850 # kg/m^3 (density of ASTM A36 sheet metal)
volume = 3.14159 * optimal_radius * optimal_radius * optimal_height / 1000 # Convert to liters
weight = density_astm_a36 * volume
# Calculate the cost of the tank (based on material price per kg)
material_price = 500000 / weight # Rp/kg (maximum allowed cost divided by weight)
cost = weight * material_price
# Print the optimal solution with units
print(f"Optimal Thickness: {optimal_thickness:.2f} mm")
print(f"Optimal Radius: {optimal_radius:.2f} mm")
print(f"Optimal Height: {optimal_height:.2f} mm")
print(f"Cost: {cost:.2f} Rp")
The result of the code is:
Optimal Thickness: 5.00 mm Optimal Radius: 24.28 mm Optimal Height: 100.00 mm Cost: 500000.00 Rp
Design Modelling
After finding out the optimum design using the code above, i try to create the 3D Design using Autodesk Inventor: