Final Report of Hydrogen Storage Optimization Project, Darell Jeremia Sitompul, 6 Juni 2023
Requirement:
- Capacity = 1 Liter
- Budget = Rp.500.000,00 (Lima ratus ribu rupiah)
First of all, to start doing the calculation, I would like to imagine the ideal shape for a hydrogen storage. My assumption would be a form of a capsule.
Here is the visualization model.
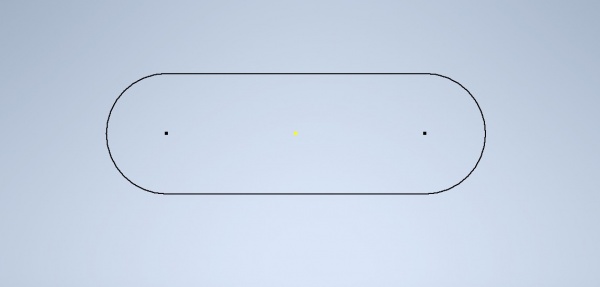
And the cross section 2 dimensional view from the centerline will look like this.
We need to optimize the storage surface area to a minimum and keep the volume at 1 liter. The storage space volume is fixed at 1 liter, but there are many combinations of radius and flat tube height. We can use programming to help us save alot of calculation time.
Finding Smallest Surface Area of the capsule with radius from 0 to 20 centimeters
Here is the code:
import numpy as np
print(": Radius : Surface Area :")
r_max = 20
a = np.zeros((r_max, 2))
for r in range (1, r_max + 1):
flat_tube_height = (1000-((4*np.pi*r**3)/3))/(np.pi*(r)**2)
sur_area = ((2*np.pi*r) * flat_tube_height) + ((2*np.pi*r**2)*2)
a[r-1][0] = int(r)
a[r-1][1] = np.round(sur_area, 5)
print(": ", a[r-1][0], " "*(6 - len(str(a[r-1][0]))),
" : ", a[r-1][1], " "*(12 - len(str(a[r-1][1]))), " :")
b = a
for i in range(len(b)):
for j in range (len(b)):
if b[i][1] < b[j][1]:
for n in range (2):
temp = b[i][n]
b[i][n] = b[j][n]
b[j][n] = temp
print("Minimum surface area will be found when")
print("Radius = ", b[0][0])
print("Surface Area : ", b[0][1])
When we run the program, the result will be shown like this
: Radius : Surface Area : : 1.0 : 2004.18879 : : 2.0 : 1016.75516 : : 3.0 : 704.36578 : : 4.0 : 567.02064 : : 5.0 : 504.71976 : : 6.0 : 484.12978 : : 7.0 : 490.96501 : : 8.0 : 518.08257 : : 9.0 : 561.51423 : : 10.0 : 618.87902 : : 11.0 : 688.6618 : : 12.0 : 769.85246 : : 13.0 : 861.7517 : : 14.0 : 963.86002 : : 15.0 : 1075.81113 : : 16.0 : 1197.33029 : : 17.0 : 1328.20743 : : 18.0 : 1468.27914 : : 19.0 : 1617.41642 : : 20.0 : 1775.51608 : Minimum surface area will be found when Radius = 6.0 Surface Area : 484.12978
We see that there is a decrease and increase in the value of the capsule area from radius 5 cm to 6 cm and from radius 6 cm to 7 cm respectively. We can find more precise result of the minimum surface area by reducing the radius range only from 5 cm to 7 cm.
We can use smaller difference of radius within iterations than the first program from 1 cm difference by each iterations to 10^(-5) cm difference.
Here is the code:
import numpy as np
a = []
r = 5
while True:
flat_tube_height = (1000-((4*np.pi*r**3)/3))/(np.pi*(r)**2)
sur_area = ((2*np.pi*r) * flat_tube_height) + ((2*np.pi*r**2)*2)
a.append((sur_area, r))
r += 1e-5
if r > 7:
break
print(min(a))
When we run the program, the result is being shown like below:
(483.5975862052437, 6.203499999954438)
The numerically minimum surface area can be obtained when the radius is about 6.20349 cm and the value of numerically minimum surface area is about 483.59758 cm^2.
Now we need to find the thickness of our material so that the storage could withstand the pressure of the hydrogen inside.
The material chosen is Aluminum 6061-T6 that has yield strength at least 240 MPa.
Let's calculate theoretical hoop stress of the required hydrogen gas pressure using Python program.
import numpy as np
print(": Thickness (mm) : Hoop Stress (MPa) :")
r = 6.20349e-2
p = 0.8
t = 1
mylist = []
while t < 14:
circumferential = (r * p * 1000)/(t)
mylist.append((t,circumferential))
print(": ", mylist[t-1][0], " "*(6 - len(str(mylist[t-1][0]))),
" : ", np.round(mylist[t-1][1],5), " "*(11 - len(str(np.round(mylist[t-1][1],5)))), " :")
t += 1
And we get the following result
: Thickness (mm) : Hoop Stress (MPa) : : 1 : 49.62792 : : 2 : 24.81396 : : 3 : 16.54264 : : 4 : 12.40698 : : 5 : 9.92558 : : 6 : 8.27132 : : 7 : 7.0897 : : 8 : 6.20349 : : 9 : 5.51421 : : 10 : 4.96279 : : 11 : 4.51163 : : 12 : 4.13566 : : 13 : 3.81753 :
We see that the thinnest option of the