Dzakiyya Yumna Fitrasani
Contents
Introduction
Hello, my name is Dzakiyya. I am a student in Metode Numerik-01. This will be my page regarding Metode Numerik.
FULLNAME: Dzakiyya Yumna Fitrasani
STUDENT NUMBER: 2106728055
Numerical Methods in Mechanical Engineering / 22 May 2023
Numerical methods are extensively used in various areas of mechanical engineering to solve complex mathematical equations, simulate physical phenomena, and optimize designs. Here are some key applications of numerical methods in mechanical engineering:
1. Solving Equations: Numerical methods such as root-finding algorithms (e.g., Newton-Raphson method) and numerical integration techniques (e.g., Simpson's rule, trapezoidal rule) are used to solve equations encountered in mechanical engineering, such as finding the roots of nonlinear equations or evaluating integrals in engineering analysis.
2. Finite Element Analysis (FEA): FEA is widely used in mechanical engineering for structural analysis. It involves dividing a complex structure into smaller finite elements and solving the equations of equilibrium numerically. FEA helps in determining stress, strain, deformation, and failure criteria in mechanical components and systems. It is used in the design and optimization of structures, such as buildings, bridges, and machine components.
3. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): CFD is employed to analyze fluid flow and heat transfer in mechanical systems. Numerical methods, such as finite volume or finite element methods, are used to discretize the fluid domain and solve the governing equations (e.g., Navier-Stokes equations). CFD is applied in the design of aerodynamic profiles, HVAC systems, combustion chambers, and optimization of fluid flow in pipes and channels.
4. Optimization and Design: Numerical optimization techniques, such as genetic algorithms, gradient-based methods, and response surface methods, are employed to optimize designs in mechanical engineering. These methods help in finding optimal solutions for parameters like shape, size, material selection, and operating conditions, considering constraints and objective functions.
These are just a few examples of how numerical methods are applied in mechanical engineering. These methods enable engineers to solve complex problems, make informed design decisions, optimize performance, and reduce the need for costly physical experiments.
Hydrogen Storage Design and Optimization
Hydrogen Storage Technologies
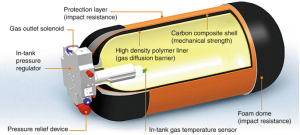
Storing hydrogen in gaseous form requires two main components – a storage compartment and a compressor to achieve higher storage pressure and increase the storage density. Gaseous hydrogen is usually not stored in pressure exceeding 100 bar in vessels above ground and 200 bar for underground storage (Wolf, 2015). The low density of hydrogen leads to the requirement of large storage volumes, and as a consequence, usually large investment costs. However, higher pressure e.g. 700 bar requires advanced vessel materials such as carbon fiber, which makes it very expensive and not considered viable for large-scale applications (Andersson & Grönkvist, 2019). One of the main advantages of storing hydrogen as compressed gas compared to liquid hydrogen is that most applications for hydrogen today require hydrogen in gaseous form.
Desain dan Optimasi Hydrogen Storage
Untuk desain dan optimisasi Hydrogen Storage bertekanan 8 bar dengan kapasitas 1 liter dan budget maksimal Rp500.000, berikut beberapa pilihan yang dapat dipertimbangkan:
1. Wadah Penyimpanan Portabel: Pilih wadah penyimpanan hidrogen portabel yang dirancang khusus untuk kapasitas 1 liter dan tekanan 8 bar. Pilihlah wadah yang terbuat dari bahan komposit yang kuat dan ringan dengan harga yang terjangkau. Beberapa wadah penyimpanan hidrogen portabel yang tersedia di pasaran adalah tabung gas kecil atau botol tekanan tinggi yang dirancang untuk aplikasi portabel.
2. Sistem Pipa Sederhana: Desain sistem pipa yang sederhana dengan material pipa dan katup yang terjangkau namun memiliki kekuatan yang memadai untuk menangani tekanan 8 bar. Pastikan sistem pipa tersebut dipasang dengan rapat dan bebas kebocoran untuk menjaga efisiensi penyimpanan.
3. Sistem Pemantauan Sederhana: Pasang sistem pemantauan sederhana seperti manometer tekanan yang terjangkau untuk memantau tekanan hidrogen dalam wadah penyimpanan. Ini akan membantu memastikan tekanan tetap dalam kisaran yang aman.
4. Penggunaan Material yang Terjangkau: Cari material yang terjangkau namun tetap memenuhi standar keamanan dan kompatibilitas dengan hidrogen. Misalnya, pipa dan katup yang terbuat dari baja karbon atau kuningan yang lebih terjangkau dibandingkan dengan material komposit.
5. Penanganan yang Aman: Selalu pertimbangkan aspek keamanan dalam desain penyimpanan hidrogen. Pastikan wadah penyimpanan ditempatkan pada area yang aman dan dilindungi dari kerusakan fisik atau paparan suhu ekstrem. Gunakan tanda peringatan yang sesuai untuk memberi tahu orang-orang tentang adanya bahaya hidrogen.
Dengan budget terbatas, pilihan dan opsi desain mungkin terbatas. Pastikan tetap memprioritaskan keamanan dalam desain. Selalu ikuti regulasi dan pedoman keselamatan yang berlaku untuk penyimpanan hidrogen.