Aqiel Saiful Fatah
Impulse and Reaction Turbines
Steam turbines are the most used mover in power plants, refineries, and processing plants. Based on the operating principle the steam turbine can be classified as these two types;
1. Impulse turbine
2. Reaction turbine
Impulse Turbines
Impulse steam turbines consists of stationary steam nozzles and a rotor with rotating buckets. What happens when the steam passes through these nozzles is hit the buckets at a high velocity causing the rotor to rotate at a high speed. In the nozzle, pressure, and enthalpy of the steam decreases whilst velocity, and volume of the steam increases.
Pressure energy is converted into kinetic energy through these nozzles. There are two types of nozzles;
1. Convergent nozzles, which are used for smaller pressure drops and develops eddy-currents
2. Convergent-divergent nozzles, which prevent eddy current and cause larger pressure drops
Impulse Principle: High pressure steam enters a stationary nozzle of a steam turbine and exits in the form of a high-speed jet. This will then hit the shaped turbine blade and the flow direction will change. The change in direction will produce an impulse force, which will cause the blade to move and the rotor to rotate.
In impulse turbines, pressure drops and velocity increases when steam passes through the nozzles. When steam passes through the blades, velocity drops but pressure is constant. This is the distinguishing feature of an impulse turbine; pressure at the inlet of the blades is equal to the outlet.
Reaction Turbines
Quite different to impulse turbines, reaction turbines have steam expand through its moving blades thus resulting in a reaction force that moves the rotor.
A reaction turbine has rows of fixed blades and moving blades that alternate in its position. Steam expands in the fixed blades first to increase its velocity as it drops in pressure. Then steam enters the moving blade rows where its direction is changed and results in an impulse force which moves the blade. Whilst moving the blade, steam expands further and drops its pressure even more giving a reaction force to the blades. Steam pressure drops in both fixed and moving blades, where the absolute velocity increases in fixed blade rows and decreases in moving blade rows. The distinguishing feature of reaction turbines is that pressure is different between the inlet of the moving blades and the outlet of the moving blades. Also, there is a n unbalanced thrust will be developed onto the rotor, which needs special adjustments.
Difference between Impulse and Reaction Turbines
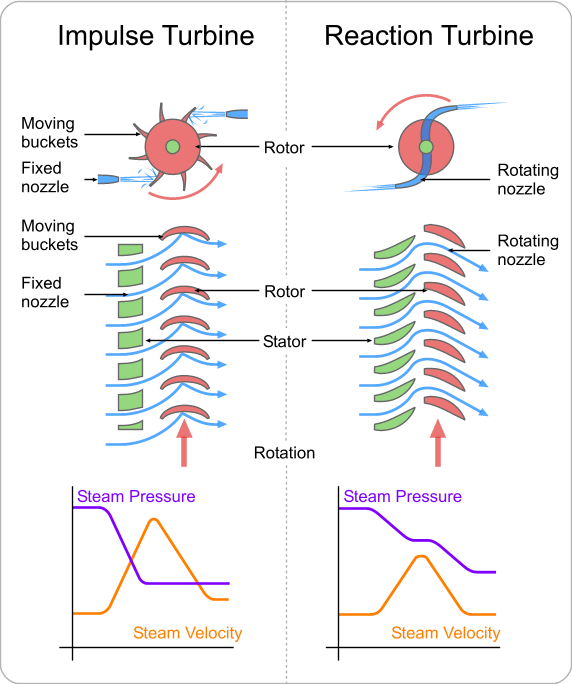
source: [1]
The Need For A Small Generator
To find out the need for our portable generator, two routes were taken. The first being searching the internet for the need of a portable generator, and the second is conducting a survey towards our target audience, which are people who are enthusiastic towards travelling, hiking, and alike.
When searching the internet, results weren't satisfactory. There were no sources to say that travelling and hiking enthusiasts require a portable generator. However, there were two products that has the same concept as ours, which is already available to the public [2][3]
Our survey was conducted online through Google Forms, and the results are as follows;
Our survey participants have an age range of 19-24 with 66.7% of them are male, and 88.9% of participants are University Students. From this we receive that 88.9% of participants agree that there is a need for a portable generator. Participants state that its usage is for charging smartphones, radios, cameras, flashlights, drones, and GPS. Their preferred size for the device is something that can fit into a daypack.