Alvian Choiri Apriliansyah
My name is Alvian Choiri Apriliansyah (2006517751), a Universitas Indonesia student from Mechanical Engineering (2020 batch, International class). Currently I'm in 6th semester, studying Energy Conversion System 2 classes amongst others
Week 1
ECS 02 ChatGPT conversation
What's the relations between sugar factory, electric vehicles, and fossil fuels?
In short, ChatGPT explains that sugar factories can produce biofuels, either for vehicles or powerplant. It also explained the reductions in fossil fuels through the electricity for electric vehicles, but it noted the EVs impact depends on powerplant source as most still uses fossils
I then read some research paper & news article about ethanol, and I asked some intriguing question: But I found the recent research from University of Wisconsin a year ago, concluded that ethanol actually produce 24% more GHG than gasoline because of land usage from producing corn
It admit the results of those research paper, saying that the increase of land usage results in more GHG (Green House Gases), but then it stated that it's still under a debate as not all papers have the same conclusion
Week 2 Friday
In this time, I learned about IC (Internal Combustion) engine modelling via OpenModelica. The teacher put out a step-by-step on
1. The OpenModelica version,
2. OMEdit IC engine model (with equations) already pre-installed
3. Explanation about the components (input: fuel & air, cooling: air/water, output: flue gas (carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, etc.))
4. Adding sinks to each of those 4 components, with additional pressure loss component for cooling section
Week 3 Tuesday
Professor Adi explains to us the pyrolisis by (literally) burning a piece of paper. I then explains to him (which he affirms) the difference with internal combustion engine that instead of using liquid fuel it uses solid fuel, example: woods, coals, etc. But of course, both processes involves a fire triangle (oxidizer, fuel, and ignition source) and produces energy & heat (exoterm).
One of the interesting application of pyrolisis is converting plastic waste into useful fuel, which unfortunately still less implemented in Indonesia (explained by Prof) due to lack of knowledge within the public about the process & benefits involved in conversion (breaking down of C-H bond in plastic into liquid fuel). Our friends from 2019 batch explains their activities in exchange period (Denmark, South Korea) when they learned how garbage separation works in other countries (either by machine, or by the public awareness/rewards themselves)
Prof then explains the data network generations (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G) & emphasize the importance of frequency (wave) in ever changing/improvements in technologies (even faster data) which has been realized since Nikola Tesla developed his inventions
Next, Professor DAI explains the principle of energy, in which "Energy can't be created, nor destroyed" explained numerically by equation (dE/dt = Q + W) in the system (can either releasing works & heat, or receiving work & heat), which he said is a root for all more complex equations/derivations
E = Energy, t = time, W = work, Q = heat
Week 3 Friday
Project synopsis: Explanations on SpaceX's decision of choosing methane (particularly from Energy Conversion standpoint)
 I decided to choose rocket engine specifically Raptor, because it's also one of the type of internal combustion engine by definition (according to Britannica). I had long been interested in SpaceX especially with its new Starship rocket, and I want to know how the selection of methane as a fuel can bring more advantages (lift more payload) compared to hydrogen even though the latter is more efficient, especially from energy conversion standpoint
I decided to choose rocket engine specifically Raptor, because it's also one of the type of internal combustion engine by definition (according to Britannica). I had long been interested in SpaceX especially with its new Starship rocket, and I want to know how the selection of methane as a fuel can bring more advantages (lift more payload) compared to hydrogen even though the latter is more efficient, especially from energy conversion standpoint
Today's classes is held by two lecturer's assistants (and later Prof. Adi). They're reviewing about combustion (thermochemical & biochemical), also the type of method based on product results (gasification, liquid, combustion)
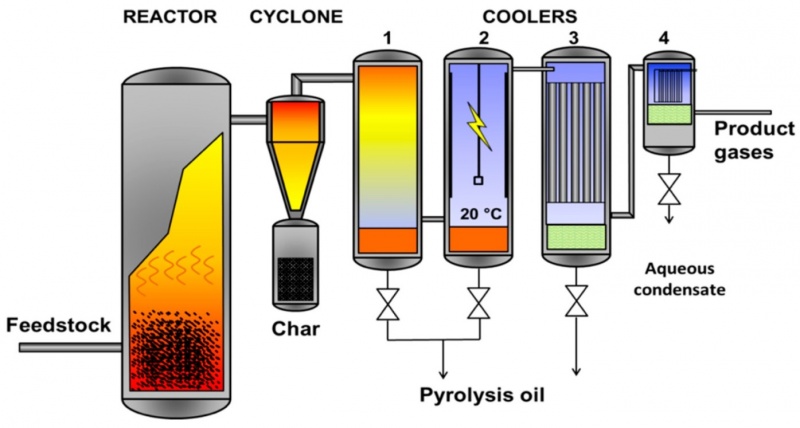
Pyrolysis stated by them is a combustion with lack of oxygen (otherwise it won't be decomposed). To be used in this, biomasses has to be dried & chopped first to maximize the amount of energy produced. It also need either constant heat (thermochemical) or catalyst (biochemical). The advantages are the variety of products that we can focused on (either gas or liquid). The general processes is as follows:
1. Feedstock (dried & chopped biomass) and heat (specific case: emissions from gensets/motors) enter the system
2. Charcoal/biochar is produced as solid product
3. Gas is produced, then enters the condenser. Non-condensable gas out as gas product, and condensed liquid (oil) out as liquid product
Picture source: Fast Pyrolysis of Poultry Litter in a Bubbling Fluidised Bed Reactor: Energy and Nutrient Recovery by Daya Shankar Pandey, Giannis Katsaros, Christian Lindfors, James J. Leahy, Savvas A. Tassou
Exact pyrolysis depends on specific case basis & products, especially regarding heating rate, biomass particle size, etc.
Prof. Adi then tells us his story his contribution to Chinese government's project developing desalination plant (converting sea water to potable one), and his tour across China (including to Three Brothers Dam)
The assistant then present to us about the modeling of pyrolysis in OpenModelica. He reiterate the earlier points about the number of components & products (listed similar to above pic), with a goal to optimize the output. He do it by increasing the reactor's temperature to 500-600 degrees celsius to produce more syn gases. He also adjust the biomass (azola) input (deleting the water concentration). The syn gases produced has to also be tested to make sure it's in right composition for later usage. We also have to know about the temperature on both input & output (products & flue gases) to determine the optimization
Week 4 Tuesday
Prof. Adi give us an overview about the topics from previous meeting. He tell us about his invitation with Pertamina & industry about the gas supply production from gasification (pyrolysis)
He also discuss about the desalination consideration in Indonesia, especially the condition of contaminated sea water in Jakarta & Thousands Islands (ship digging the trashes/debris on the sea). Not many parties in Indonesia that are seriously pursuing the desalination project. The usual process of filtering is mechanical, but there's a recent advancement by using graphene (filtered to atomic levels) which is more effective.
Talking about biomass, he stated the benefits & examples of biochar production in Indonesian farmer community. He explained that all of our world is consists of carbon, and vibration.
The conclusion is that, it's important to increase awareness (especially in Indonesia) about the wiser usage of energy conversion, especially desalination & biomasses, to create a better life with reduced greenhouses, other negative environmental impacts, and more benefits for community.
Week 5 Tuesday
Three students from our class present about their projects, mostly talking about cars engine. But I'm planning to do something a little different about the project. I explained to Prof. DAI that I'm choosing rocket engine (Raptor) because I'm interested in SpaceX/NASA for a while, and rocket engine is also a type of Internal Combustion engine.
Then Prof. DAI explained that it's very important to have a direct observation about the phenomenon related to rocket, especially the Newton's Third Law (Action = Reaction) and combustion, but obviously in Indonesia we don't have any real rocket engine let alone in my own house. So he suggested me that a simple demonstration by blowing & flying a balloon would be enough for this project, in which then I concur with the explanation.