Moh Khairul Imam Assidiqqi
السَّلاَمُ عَلَيْكُمْ وَرَحْمَةُ اللهِ وَبَرَكَاتُهُ
| Profile | |
|---|---|

| |
| Nama Lengkap | Moh Khairul Imam Assidiqqi |
| NPM | 1906301210 |
| Jurusan | Teknik Mesin |
| Alamat Email | moh.khairul@ui.ac.id |
Contents
Perkenalan Singkat
Assalamu'alaikum Wr. Wb. Perkenalkan nama saya Moh Khairul Imam Assidiqqi. Saya adalah mahasiswa Departemen Teknik Mesin angkatan 2019.
Pertemuan Pertama Metode Numerik (11-11-2020)
Pada hari Rabu, 11 November 2020 adalah pertemuan pertama kelas Metode Numerik bersama Pak Dr. Ir. Ahmad Indra Siswantara. Pak Dai memberikan penjelasan terlebih dahulu bagaimana cara menggunakan Wiki AIR. Kemudian beliau menjelaskan apa itu metode numerik dan untuk apa kita mempelajarinya.
Ada 4 tujuan mempelajari metode numerik:
1. Memahami konsep dan prinsip dasar di dalam metode numerik.
2. Dapat menerapkan pemahaman terhadap konsep di dalam permodelan numerik.
3. Mampu menerapkan metode numerik di dalam persoalan keteknikan.
4. Mendapat nilai tambah sehingga menjadi orang yang beradab.
Setelah itu Pak Dai menjelaskan secara singkat tentang Open Modelica.
Tugas 1 Metode Numerik
Sebelum kelas berakhir, Pak Dai memberikan kami tugas untuk mempelajari Open Modelica. Setelah itu kami ditugaskan untuk membuat video tutorial cara menggunakan Open Modelica.
Berikut adalah hasil tugas saya:
Pertemuan Kedua Metode Numerik (18-11-2020)
Pada pertemuan kedua dengan Pak Dai, kami diberikan pelajaran yang sangat berharga bahwa kita harus menjadi orang yang beruntung. Maksudnya adalah kita harus menjalani hari ini lebih baik dari hari kemarin. Dan jangan menjadi orang yang merugi yang hari malah lebih buruk dari hari kemarin.
Setelah itu Pak Dai juga menyuruh kami untuk menayangkan tugas-tugas kami pada minggu pertama. Kami diperbolehkan bertanya apapun yang masih kami belum ketahui. Kemudian Pak Dai mengajarkan kami tentang Class dan Function di OpenModelica dan Pak Dai juga mengajarkan bahwa suatu fungsi bisa dipanggil ke sebuah kelas.
Tugas 2 Metode Numerik
Di akhir kelas, Pak Dai memberikan kami tugas untuk membuat video dimana kami diminta untuk membuat sebuah fungsi berupa persamaan aljabar simultan dengan variabel array kemudian membuat class untuk memanggil fungsi tersebut.
Berikut adalah hasil tugas saya:
function
function Gauss input Real A[5,5]; input Real B[5]; output Real X[5]; algorithm X:=Modelica.Math.Matrices.solve(A,B); end Gauss;
class
class SPL_5_Variabel
parameter Real A[5,5]=[2,-2,0,4,2;
-2,4,2,0,5;
2,-2,2,-2,0;
0,4,2,4,4;
4,2,2,4,-2];
parameter Real B[5]={2,4,6,8,-12};
Real X[5];
equation
X=Gauss(A,B);
end SPL_5_Variabel;
Pertemuan Ketiga Metode Numerik (25-11-2020)
Pada pertemuan ketiga, Pak Dai memaparkan tiga aplikasi metode numerik yang sering digunakan dalam menyelesaikan permasalahan teknik, pertama ada Computation Fluid Dynamics (CFD), lalu Finite Element Analysis, dan Metode Stokastik. Setelah itu Pak Dai meminta beberapa mahasiswa untuk mereview tugas-tugas yang telah diberikan sebelumnya. Salah satu teman kami yaitu Josiah memberikan sharing mengenai aljabar simultan dan variabel array.
Kemudian Pak Dai menjelaskan kembali mengenai metode Gauss. Pak dai mendorong kami untuk membuat code sendiri untuk menyelesaikan Gauss Jordan. Salah satu mahasiswa, yaitu Cristo memberikan sharing mengenai code yang telah ia buat untuk Gauss Jordan, berikut code modelica untuk Gauss Jordan dari Cristo:
// Gauss-Jordan Algorithm // Transforms input matrix A into reduced row echelon form matrix B // Christopher S.E. November 2020 input Real [:,:] A; // An augmented matrix of m*n output Real [:,:] B; // Output matrix in reduced row echelon form // Local variables
protected Integer h = 1; // Initialize pivot row Integer k = 1; // Initialize pivot column Integer m = size(A,1); // Number of rows in matrix Integer n = size(A,2); // Number of columns in matrix Integer c = 0; // Index counter Integer max_row; // Row index of max number in pivot column
Real [:] pivot_column; // Vector containing pivot column data Real [:] pivot_row; // Vector containing backwards pivot row data Real [:,:] temp_array; // Stores matrix data when switching rows Real r; // Ratio value used for row operations
// Limit to handle floating point errors Real float_error = 10e-10;
algorithm
// Transfer input matrix A into variable B B := A;
while h <= m and k <= n loop
// Dealing with floating point errors
for i in 1:m loop
for j in 1:n loop
if abs(B[i,j]) <= float_error then
B[i,j] := 0;
end if;
end for;
end for;
// Finding the pivot
pivot_column := {B[i,h] for i in h:m};
// Get position index of lowest row with greatest pivot number
c:= h-1;
for element in pivot_column loop
c := c+1;
if abs(element) == max(abs(pivot_column)) then
max_row := c;
end if;
end for;
// No pivot in this column, move on to next column
if B[max_row, k] == 0 then
k := k+1;
else
// Swap Rows h <-> max_row
temp_array := B;
temp_array[h] := B[max_row];
temp_array[max_row] := B[h];
B:= temp_array;
// Divide pivot row by pivot number
B[h] := B[h]/B[h,k];
// For all rows below the pivot
for i in (h+1):m loop
// Store the ratio of the row to the pivot
r := B[i,k] / B[h,k];
// Set lower part of pivot column to zero
B[i,k] := 0;
// Operations on the remaining row elements
for j in (k+1):n loop
B[i,j] := B[i,j] - B[h,j] * r;
end for;
end for;
// Move on to next pivot row and column
h := h+1;
k := k+1;
end if;
end while;
// The matrix is now in row echelon form
// Set values of (h,k) to (m,n) h := m; k := n;
while h >= 1 and k >=1 loop
// Dealing with floating point errors
for i in 1:m loop
for j in 1:n loop
if abs(B[i,j]) <= float_error then
B[i,j] := 0;
end if;
end for;
end for;
// Finding the pivot
pivot_row := {B[h,i] for i in 1:k};
// Get position index k of pivot
c := 0;
for element in pivot_row loop
c := c+1;
if element <> 0 then
break;
end if;
end for;
k := c;
// No pivot in this row, move on to next row
if B[h, k] == 0 then
h := h-1;
else
// Perform row operations
for i in 1:(h-1) loop
r := B[i,k];
B[i] := B[i] - B[h] * r;
end for;
// Move on to next pivot row and column
h := h-1;
k := k-1;
end if;
end while;
// The matrix is now in reduced row echelon form
end GaussJordan;
Tugas 3 Metode Numerik
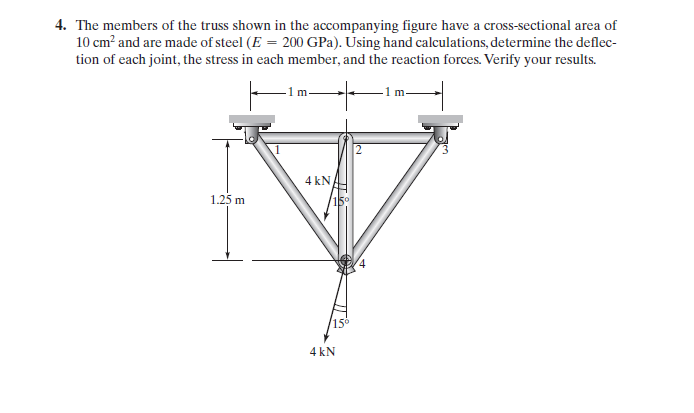
Di akhir kelas, Pak Dai memberikan kami tugas yaitu menyelesaikan persoalan berikut:
Berikut adalah penyelesaiannya:
class Trusses
parameter Integer N=8; //Global matrice = 2*points connected
parameter Real A=0.001; //Area m2
parameter Real E=200e9; //Pa
Real G[N,N]; //global
Real Ginitial[N,N]; //global
Real Sol[N]; //global dispplacement
Real X[N]={0,0,-1035.2762,-3863.7033,0,0,-1035.2762,-3863.7033};
Real R[N]; //global reaction force
Real SolMat[N,1];
Real XMat[N,1];
//boundary condition
Integer b1=1;
Integer b2=3;
//truss 1
parameter Real X1=0; //degree between truss
Real k1=A*E/1;
Real K1[4,4]; //stiffness matrice
Integer p1a=1;
Integer p1b=2;
Real G1[N,N];
//truss 2
parameter Real X2=0; //degree between truss
Real k2=A*E/1;
Real K2[4,4]; //stiffness matrice
Integer p2a=2;
Integer p2b=3;
Real G2[N,N];
//truss 3
parameter Real X3=90; //degree between truss
Real k3=A*E/1.25;
Real K3[4,4]; //stiffness matrice
Integer p3a=2;
Integer p3b=4;
Real G3[N,N];
//truss 4
parameter Real X4=90+38.6598; //degree between truss
Real k4=A*E/1.6;
Real K4[4,4]; //stiffness matrice
Integer p4a=1;
Integer p4b=4;
Real G4[N,N];
//truss 5
parameter Real X5=90-38.6598; //degree between truss
Real k5=A*E/1.6;
Real K5[4,4]; //stiffness matrice
Integer p5a=3;
Integer p5b=4;
Real G5[N,N];
/*
for each truss, please ensure pXa is lower then pXb (X represents truss element number)
*/
algorithm
//creating global matrice
K1:=Stiffness_Matrices(X1);
G1:=k1*Local_Global(K1,N,p1a,p1b);
K2:=Stiffness_Matrices(X2);
G2:=k2*Local_Global(K2,N,p2a,p2b);
K3:=Stiffness_Matrices(X3);
G3:=k3*Local_Global(K3,N,p3a,p3b);
K4:=Stiffness_Matrices(X4);
G4:=k4*Local_Global(K4,N,p4a,p4b);
K5:=Stiffness_Matrices(X5);
G5:=k5*Local_Global(K5,N,p5a,p5b);
G:=G1+G2+G3+G4+G5;
Ginitial:=G;
//implementing boundary condition
for i in 1:N loop
G[2*b1-1,i]:=0;
G[2*b1,i]:=0;
G[2*b2-1,i]:=0;
G[2*b2,i]:=0;
end for;
G[2*b1-1,2*b1-1]:=1;
G[2*b1,2*b1]:=1;
G[2*b2-1,2*b2-1]:=1;
G[2*b2,2*b2]:=1;
//solving displacement
Sol:=Gauss_Jordan(N,G,X);
//solving reaction force
SolMat:=matrix(Sol);
XMat:=matrix(X);
R:=Reaction_Trusses(N,Ginitial,SolMat,XMat);
end Trusses;Fungsi Panggil
function Reaction_Trusses
input Integer N;
input Real A[N,N];
input Real B[N,1];
input Real C[N,1];
Real X[N,1];
output Real Sol[N];
Real float_error = 10e-10;
algorithm
X:=A*B-C;
for i in 1:N loop
if abs(X[i,1]) <= float_error then
X[i,1] := 0;
end if;
end for;
for i in 1:N loop
Sol[i]:=X[i,1];
end for;
end Reaction_Trusses;function Local_Global
input Real Y[4,4];
input Integer B;
input Integer p1;
input Integer p2;
output Real G[B,B];
algorithm
for i in 1:B loop
for j in 1:B loop
G[i,j]:=0;
end for;
end for;
G[2*p1,2*p1]:=Y[2,2];
G[2*p1-1,2*p1-1]:=Y[1,1];
G[2*p1,2*p1-1]:=Y[2,1];
G[2*p1-1,2*p1]:=Y[1,2];
G[2*p2,2*p2]:=Y[4,4];
G[2*p2-1,2*p2-1]:=Y[3,3];
G[2*p2,2*p2-1]:=Y[4,3];
G[2*p2-1,2*p2]:=Y[3,4];
G[2*p2,2*p1]:=Y[4,2];
G[2*p2-1,2*p1-1]:=Y[3,1];
G[2*p2,2*p1-1]:=Y[4,1];
G[2*p2-1,2*p1]:=Y[3,2];
G[2*p1,2*p2]:=Y[2,4];
G[2*p1-1,2*p2-1]:=Y[1,3];
G[2*p1,2*p2-1]:=Y[2,3];
G[2*p1-1,2*p2]:=Y[1,4];
end Local_Global;function Stiffness_Matrices
input Real A;
Real Y;
output Real X[4,4];
Real float_error = 10e-10;
final constant Real pi=2*Modelica.Math.asin(1.0);
algorithm
Y:=A/180*pi;
X:=[(Modelica.Math.cos(Y))^2,Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y),-(Modelica.Math.cos(Y))^2,-Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y);
Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y),(Modelica.Math.sin(Y))^2,-Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y),-(Modelica.Math.sin(Y))^2;
-(Modelica.Math.cos(Y))^2,-Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y),(Modelica.Math.cos(Y))^2,Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y);
-Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y),-(Modelica.Math.sin(Y))^2,Modelica.Math.cos(Y)*Modelica.Math.sin(Y),(Modelica.Math.sin(Y))^2];
for i in 1:4 loop
for j in 1:4 loop
if abs(X[i,j]) <= float_error then
X[i,j] := 0;
end if;
end for;
end for;
end Stiffness_Matrices;function Gauss_Jordan
input Integer N;
input Real A[N,N];
input Real B[N];
output Real X[N];
Real float_error = 10e-10;
algorithm
X:=Modelica.Math.Matrices.solve(A,B);
for i in 1:N loop
if abs(X[i]) <= float_error then
X[i] := 0;
end if;
end for;
end Gauss_Jordan;Pertemuan Keempat Metode Numerik (02-12-2020)
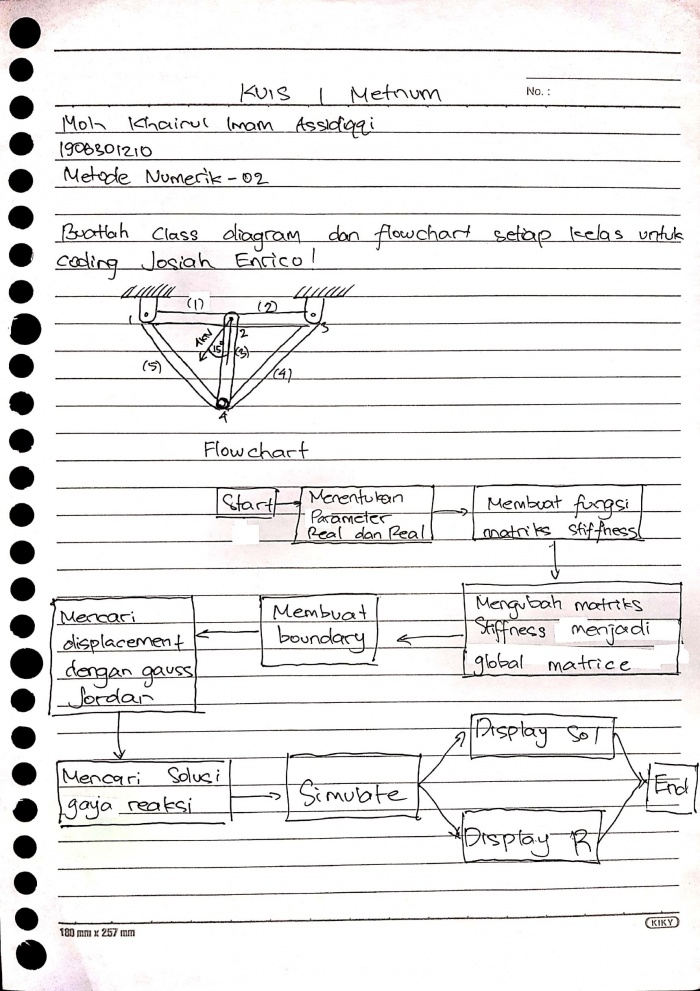
Kuis 1 Metode Numerik Diagram Class dan Flowchart
Buatlah class diagram dan flowchart setiap class untuk coding dari Josiah Enrico!
Berikut adalah jawaban saya:
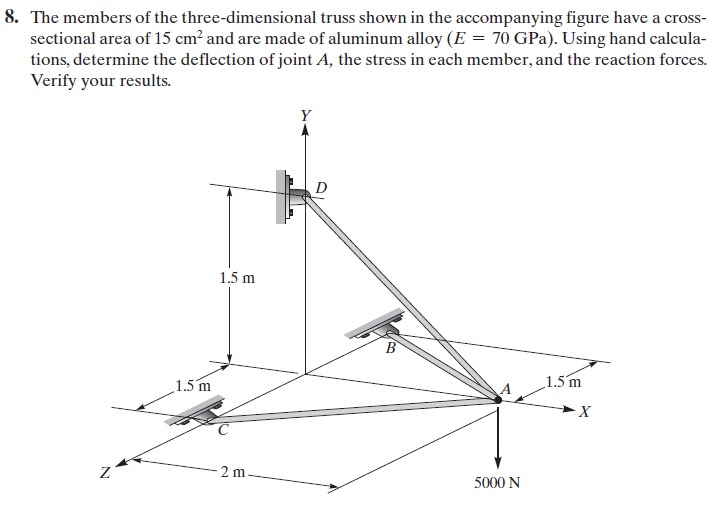
Tugas 4 Metode Numerik
Kami diminta untuk menyelesaikan persoalan Space Truss (3D) dengan membuat flowchart, diagram class, dan coding modelicanya.