Difference between revisions of "JosiahEnrico"
JosiahEnrico (talk | contribs) (→CFD Simulation for Cyclone Separator - Aplikasi Modelica/26 November 2020) |
JosiahEnrico (talk | contribs) (→CFD Simulation for Cyclone Separator - Aplikasi Modelica/26 November 2020) |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
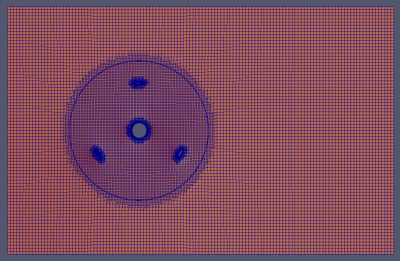
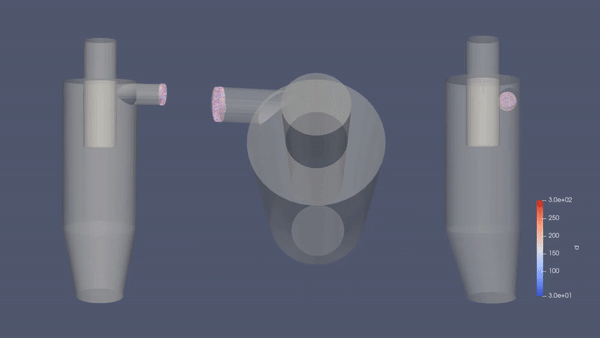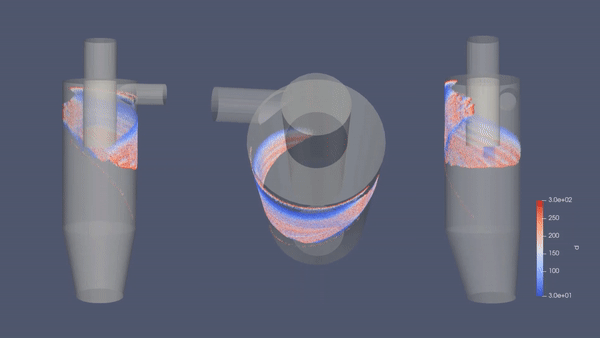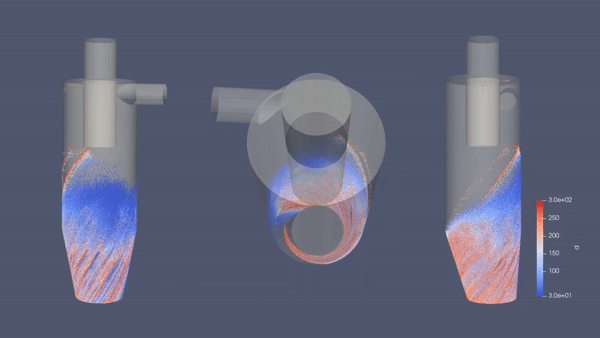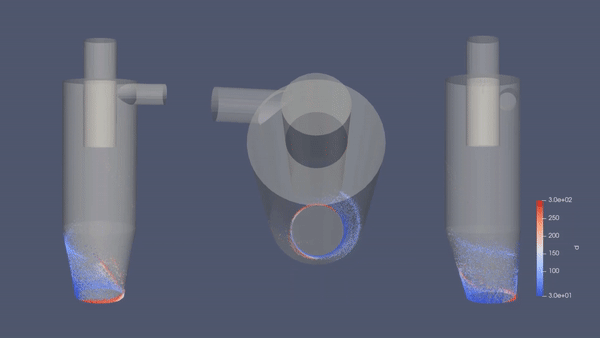
As we can see in the simulation above, the geometry of the cyclone separator will generate swiveling fluid inside the cylinder. This cyclone-like flow is developed by the tangential inlet velocity entering the geometry. While whirling along the chamber surface, gravity takes place by driving the multiphase stream downward creating a vortex. Since larger particles tend to have heavier mass relative to the density and worse compliant to the high-speed spiral motion of vortex, the particles | As we can see in the simulation above, the geometry of the cyclone separator will generate swiveling fluid inside the cylinder. This cyclone-like flow is developed by the tangential inlet velocity entering the geometry. While whirling along the chamber surface, gravity takes place by driving the multiphase stream downward creating a vortex. Since larger particles tend to have heavier mass relative to the density and worse compliant to the high-speed spiral motion of vortex, the particles | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Metode Numerik = | = Metode Numerik = | ||
Revision as of 00:18, 1 December 2020
Holaaa
Perkenalkan nama saya Josiah Enrico S dari jurusan teknik mesin FTUI. Sebagai salah seorang mahasiswa, saya senang belajar dan berbagi banyak hal baru kepada dunia. Melalui wiki ini, saya akan berbagi kepada kalian tentang apa yang saya pelajari. :)
Contents
- 1 Aplikasi CFD
- 1.1 Melakukan Simulasi Tanpa Menggunakan GUI - Aplikasi Modelica/17 November 2020
- 1.2 Contoh Aplikasi Dynamic Mesh dan 6DoF - Aplikasi Modelica/19 November 2020
- 1.3 CFD Simulation for Economizer Hopper - Aplikasi Modelica/24 November 2020
- 1.4 CFD Simulation for Cyclone Separator - Aplikasi Modelica/26 November 2020
- 2 Metode Numerik
Aplikasi CFD
Melakukan Simulasi Tanpa Menggunakan GUI - Aplikasi Modelica/17 November 2020
Contoh Aplikasi Dynamic Mesh dan 6DoF - Aplikasi Modelica/19 November 2020
VAWT atau singkatan dari Vertical Axis Wind Turbin adalah salah satu mesin tenaga yang mengubah energi mekanis dari aliran angin menjadi kerja. ciri khas mesin tipe ini adalah turbin memiliki poros yang tegak lurus dengan aliran fluida dan vertikal dengan tanah seperti gambar di samping. Desain ini memungkinkan aliran angin dari arah manapun dapat dimanfaatkan untuk menjadi kerja asalkan tidak sejajar dengan poros turbin ini. Dalam insdustri, mesin ini juga dikenal sebagai "transverse axis wind turbine" atau "cross-flow wind turbine." Dalam artikel ini, diperlihatkan simulasi komputer yang menggambarkan dinamika fluida ketika turbin sedang beroperasi (dengan variasi massa jenis).
Untuk mengimplementasikan simulasi CFD dalam desain berikut, digunakan metode Dynamic Mesh dan 6DoF (6 Degree of Freedom). Dynamic Mesh berarti mesh tidak rigid tapi fleksibel misalnya bergerak dalam suatu jalur atau berputar dalam suatu axis, sedangkan 6DoF berarti simulasi dilakukan dengan memperhatikan kebebasan gerak suatu mesh ketika dialiri fluida (Dalam 3 dimensi kebebasan ini berderajat 6)

|

|
| rho=1,2 kg/m^3 | rho=4.8 kg/m^3 |
Analisa
CFD Simulation for Economizer Hopper - Aplikasi Modelica/24 November 2020
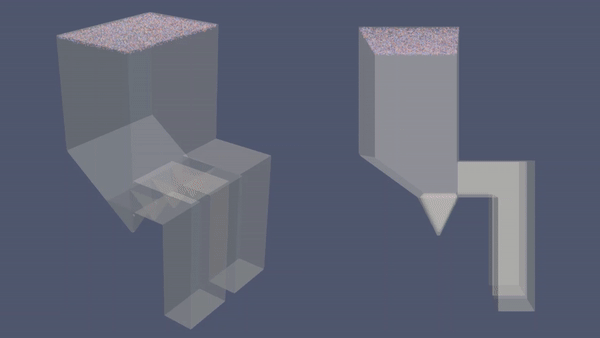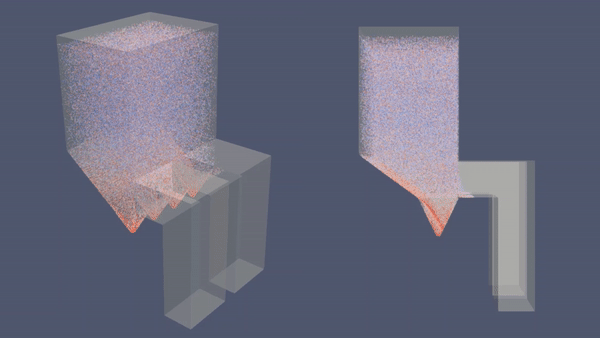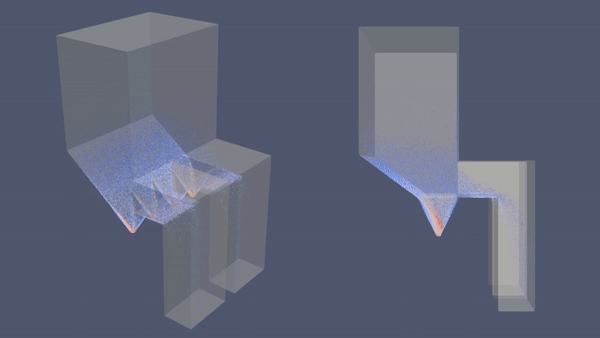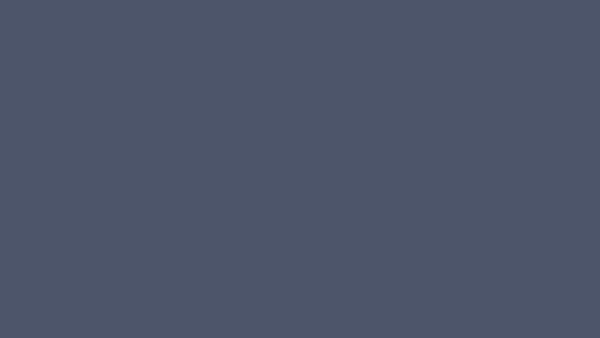
Economizer Hopper adalah salah satu fitur ducting yang biasanya terdapat dalam PLTU yang menggunakan batu bara. Fitur ini berfungsi menangkap dan menampung fly ash (abu terbang) yang dihasilkan pembakaran batu bara. Tanpa Economizer Hopper, debu tersebut bisa menimbulkan berbagai masalah operasional seperti menghambat aliran fluida di preheater, merusak blade IDF dan Guide Vane, menumpuk di ducting dan bahkan juga mencemari lingkungan. Dalam artikel ini, akan ditunjukkan simulasi CFD yang menggambarkan perbedaan efektifitas sistem yang menggunakan Economizer Hopper dan tanpa Hopper.
- Model Simulasi dalam CFD:
- 3D
- Transient
- Incompressible
- Turbulent
- No Heat Transfer
- Multi-phase
|
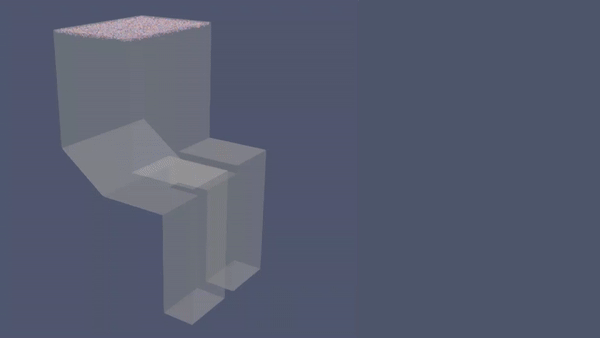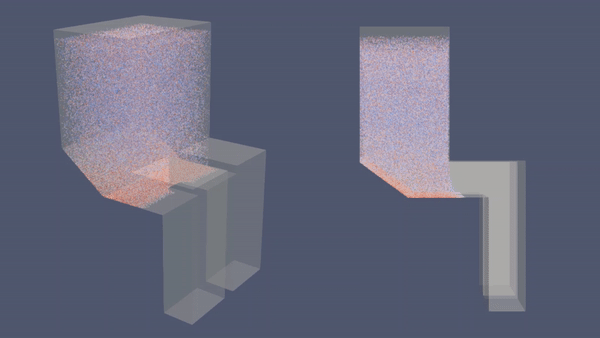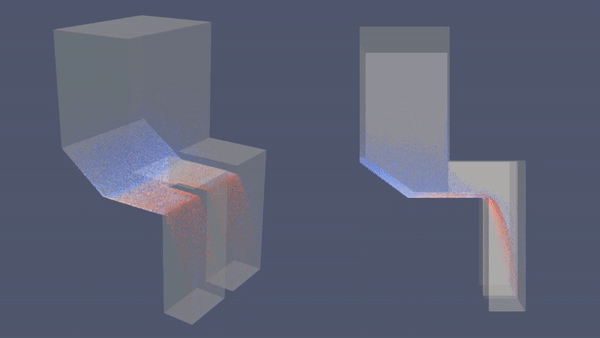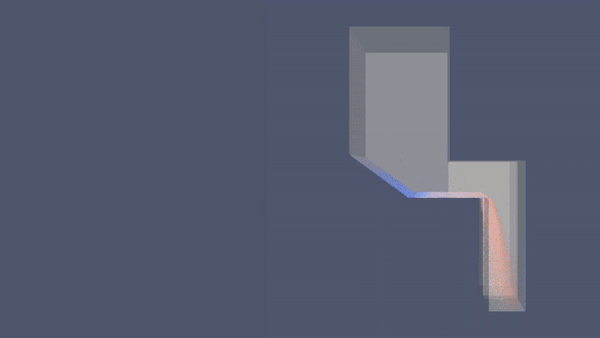
|
| Economizer dengan Hopper | Economizer tanpa Hopper |
- Analisa:
CFD Simulation for Cyclone Separator - Aplikasi Modelica/26 November 2020
Cyclone separators or simply cyclones are separation devices (dry scrubbers) that use the principle of inertia to remove particulate matter from flue gases. Cyclone separators is one of many air pollution control devices known as pre-cleaners since they generally remove larger pieces of particulate matter. This prevents finer filtration methods from having to deal with large, more abrasive particles later on. In addition, several cyclone separators can operate in parallel, and this system is known as a multi-cyclone.
It is important to note that cyclones can vary drastically in their size. The size of the cyclone depends largely on how much flue gas must be filtered, thus larger operations tend to need larger cyclones. For example, several different models of one cyclone type can exist, and the sizes can range from a relatively small 1.2-1.5 meters tall to around 9 meters —which is about as tall as a three-story building.
source: https://energyeducation.ca/encyclopedia/Cyclone_separator
Verification:
Validation:
Simulation Result:
Analysis:
As we can see in the simulation above, the geometry of the cyclone separator will generate swiveling fluid inside the cylinder. This cyclone-like flow is developed by the tangential inlet velocity entering the geometry. While whirling along the chamber surface, gravity takes place by driving the multiphase stream downward creating a vortex. Since larger particles tend to have heavier mass relative to the density and worse compliant to the high-speed spiral motion of vortex, the particles
Metode Numerik
Intro - Metode Numerik/11 November 2020
Tujuan belajar metode numerik yaitu agar penulis dapat:
1) Memahami konsep dan prinsip dasar metode numerik.
2) Memahami aplikasi metode numerik
3) Menyelesaikan persoalan teknik dengan metoda numerik
4) Mendapat nilai tambah sebagai manusia yang lebih beradab
Aplikasi Modelica - Metode Numerik/18 November 2020
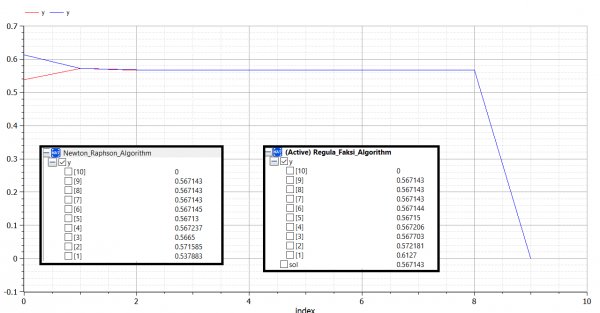
Berikut ini adalah contoh penerapan aplikasi OpenModelica untuk membuat 4 algoritma metode numerik dalam mencari roots of equation (akar persamaan) dari:
f(x) = exp^(-x)-(x)
f'(x) = -exp^(-x)-1
error maksimum = 0.0000001
1) Newton Raphson (Terbuka)
model Newton_Raphson_Algorithm parameter Real g=1; //guess parameter Integer N=20; //max iteration parameter Real er=0.0000001; //error maximum Real a[N]; Real y[N];//function Real ER[N]; //error Real sol; //solution algorithm a[1]:=g; y[1]:=a[1]-(exp(-a[1])-a[1])/(-exp(-a[1])-1); ER[1]:=abs(1-a[1]/y[1]); for i in 2:N loop a[i]:=y[i-1]; y[i]:=a[i]-(exp(-a[i])-a[i])/(-exp(-a[i])-1); ER[i]:=abs(1-y[i-1]/y[i]); if ER[i]<er then sol:=y[i]; break; end if; end for; end Newton_Raphson_Algorithm;
2) Secant (Terbuka)
model Secant_Algorithm parameter Real a=0; //guess parameter Real b=1; //guess parameter Integer N=10; //max iteration parameter Real er=0.0000001; //error maximum Real A[N]; Real B[N]; Real y[N]; Real ER[N]; Real sol; //solution algorithm A[1]:=a; B[1]:=b; y[1]:=B[1]-(exp(-B[1])-B[1])*(A[1]-B[1])/((exp(-A[1])-A[1])-(exp(-B[1])-B[1])); ER[1]:=abs(1-B[1]/y[1]); for i in 2:N loop A[i]:=B[i-1]; B[i]:=y[i-1]; y[i]:=B[i]-(exp(-B[i])-B[i])*(A[i]-B[i])/((exp(-A[i])-A[i])-(exp(-B[i])-B[i])); ER[i]:=abs(1-y[i-1]/y[i]); if ER[i]<er then sol:=y[i]; break; end if; end for; end Secant_Algorithm;
3) Bisection (Tertutup)
model Bisection_Algorithm parameter Real a=0; //guess bawah parameter Real b=1; //guess atas parameter Integer N=50; //max iteration parameter Real er=0.0000001; //error maximum Real fa=(exp(-a)-a); Real fb=(exp(-b)-b); Real A[N]; Real B[N]; Real fy[N]; Real y[N]; Real ER[N]; Real sol; //solution algorithm if fa*fb<0 then A[1]:=a; B[1]:=b; y[1]:=(A[1]+B[1])/2; fy[1]:=exp(-y[1])-y[1]; ER[1]:=1; for i in 2:N loop if fy[i-1]>0 then A[i]:=y[i-1]; B[i]:=B[i-1]; else A[i]:=A[i-1]; B[i]:=y[i-1]; end if; y[i]:=(A[i]+ B[i])/2; fy[i]:=exp(-y[i])-y[i]; ER[i]:=abs(1-y[i-1]/y[i]); if ER[i]<er then sol:=y[i]; break; end if; end for; end if; end Bisection_Algorithm;
4) Regula Falsi (Tertutup)
model Regula_Falsi_Algorithm parameter Real a=0; //guess bawah parameter Real b=1; //guess atas parameter Integer N=20; //max iteration parameter Real er=0.0000001; //error maximum Real A[N]; Real B[N]; Real fa[N]; Real fb[N]; Real fy[N]; Real y[N]; Real ER[N]; Real sol; //solution algorithm A[1]:=a; B[1]:=b; fa[1]:=exp(-A[1])-A[1]; fb[1]:=exp(-B[1])-B[1]; if fa[1]*fb[1]<0 then y[1]:=(A[1]*fb[1]-B[1]*fa[1])/(fb[1]-fa[1]); fy[1]:=exp(-y[1])-y[1]; ER[1]:=1; for i in 2:N loop if fy[i-1]>0 then A[i]:=y[i-1]; B[i]:=B[i-1]; else A[i]:=A[i-1]; B[i]:=y[i-1]; end if; fa[i]:=exp(-A[i])-A[i]; fb[i]:=exp(-B[i])-B[i]; y[i]:=(A[i]*fb[i]-B[i]*fa[i])/(fb[i]-fa[i]); fy[i]:=exp(-y[i])-y[i]; ER[i]:=abs(1-y[i-1]/y[i]); if ER[i]<er then sol:=y[i]; break; end if; end for; end if; end Regula_Falsi_Algorithm;
Berikut link Youtube yang berisi penjelasan tentang algoritma dan penulisan kode OpenModelica keempat metode diatas:
Fungsi Panggil dalam Modelica - Metode Numerik/18 November 2020
Fungsi panggil dalam aplikasi Modelica adalah metode membuat fungsi numerik dalam kelas function yang akan digunakan di dalam permodelan numerik utama (tipe 'class'). metode ini biasanya dipakai untuk menyederhanakan persoalan matematika yang kompleks, seperti persamaan aljabar simultan, sehingga lebih mudah diselesaikan. Dalam artikel ini akan ditampilkan 3 contoh persoalan numerik dengan solusi array atau lebih dari satu anggota:
1) Root of Equation (Newton Raphson dan Regula Falsi)
|
Newton Raphson ... algorithm a[1]:=g; y[1]:=a[1]-(Fungsi(a[1]))/(Der_Fungsi(a[1])); ER[1]:=abs(1-a[1]/y[1]); for i in 2:N loop a[i]:=y[i-1]; y[i]:=a[i]-(Fungsi(a[i]))/(Der_Fungsi(a[1])); ER[i]:=abs(1-y[i-1]/y[i]); if ER[i]<er then sol:=y[i]; break; end if; Regula Falsi ... fa[1]:=Fungsi(A[1]); fb[1]:=Fungsi(B[1]); if fa[1]*fb[1]<0 then y[1]:=(A[1]*fb[1]-B[1]*fa[1])/(fb[1]-fa[1]); fy[1]:=Fungsi(y[1]); ER[1]:=1; ... fa[i]:=Fungsi(A[i]); fb[i]:=Fungsi(B[i]); y[i]:=(A[i]*fb[i]-B[i]*fa[i])/(fb[i]-fa[i]); fy[i]:=Fungsi(y[i]); ER[i]:=abs(1-y[i-1]/y[i]); ... |
fungsi function Fungsi input Real X; output Real Y; algorithm Y:=exp(-X)-X; end Fungsi; fungsi turunan function Der_Fungsi input Real X; output Real Y; algorithm Y:=-exp(-X)-1; end Der_Fungsi; |
2) Heat Diffusion
Referensi: Versteeg, H. K., Malalasekera, W. (2007). An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics. 2nd Edition. Harlow: Pearson (Example 4.2)
|
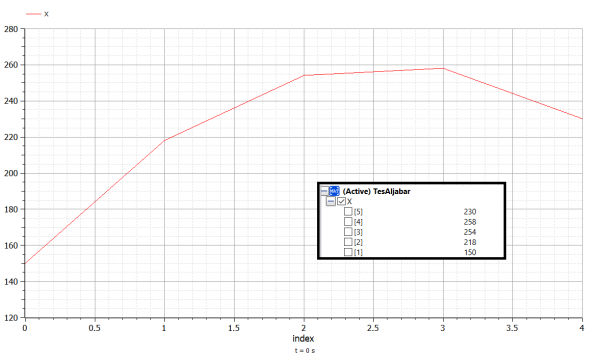
Persamaan class TesAljabar
parameter Real A[5,5]=[375,-125,0,0,0;
-125,250,-125,0,0;
0,-125,250,-125,0;
0,0,-125,250,-125;
0,0,0,-125,375];
parameter Real B[5]={29000,4000,4000,4000,54000};
Real X[5];
equation
X=matriks5(A,B);
end TesAljabar;
|
fungsi function matriks5 input Real A[5,5]; input Real B[5]; output Real X[5]; algorithm X:=Modelica.Math.Matrices.solve(A,B); end matriks5; |
3) Combined Spring Stiffness
Referensi: http://www.sharetechnote.com/html/EngMath_Matrix_FEM_ComplicatedSpring.html
|
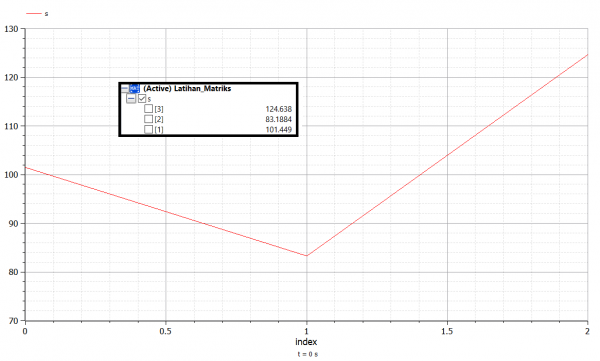
Persamaan class Latihan_Matriks
parameter Real c1=1; //spring 1
parameter Real c2=2; //spring 2
parameter Real c3=3; //spring 3
parameter Real c4=4; //spring 4
parameter Real c5=5; //spring 5
parameter Real k1[3,3]=c1*[1,0,0;
0,0,0;
0,0,0];
parameter Real k2[3,3]=c2*[1,-1,0;
-1,1,0;
0,0,0];
parameter Real k3[3,3]=c3*[1,-1,0;
-1,1,0;
0,0,0];
parameter Real k4[3,3]=c4*[1,0,-1;
0,0,1;
-1,0,1];
parameter Real k5[3,3]=c5*[0,0,0;
0,1,-1;
0,-1,1];
parameter Real B[3]={100,200,300};
Real K[3,3];
Real s[3];
algorithm
K:=k1+k2+k3+k4+k5;
s:=matriks3(K,B);
end Latihan_Matriks;
|
fungsi function matriks3 input Real A[3,3]; input Real B[3]; output Real X[3]; algorithm X:=Modelica.Math.Matrices.solve(A,B); end matriks3; |
Berikut link Youtube yang berisi penjelasan tentang algoritma dan penulisan kode OpenModelica latihan diatas:
Gate Valve - Aplikasi CFD/12 November 2020
Gate Valve
membuka atau menutup aliran
Mengatur kecepataan fluida (Regulasi)
Mangatasi Backflow atau aliran balik