Difference between revisions of "'''1. What is FCC?'''"
Agus.nuryadi (talk | contribs) |
Agus.nuryadi (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
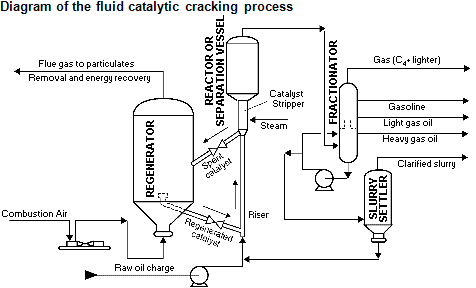
The fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) unit converts low-value heavy hydrocarbons into a series of more valuable products such as gasoline and light olefinic compounds. Higher selectivity to these intermediate products is more desirable for FCC reactor performance. | The fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) unit converts low-value heavy hydrocarbons into a series of more valuable products such as gasoline and light olefinic compounds. Higher selectivity to these intermediate products is more desirable for FCC reactor performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | FCC is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the activation energy and is often used in oil refinery process for the rupture of high molecular weight hydrocarbon chains, a process needed to optimize the proportion of gasoline produced. | ||
| + | |||
| + | FCC particles, which are designed for a fluidized bed, are a well-known example of a composite catalyst; and the situation encountered can be considered representative | ||
| + | |||
[[File:FCCdiagram.png|700px|thumb|centre|alt text]] | [[File:FCCdiagram.png|700px|thumb|centre|alt text]] | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 8 December 2020
The fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) unit converts low-value heavy hydrocarbons into a series of more valuable products such as gasoline and light olefinic compounds. Higher selectivity to these intermediate products is more desirable for FCC reactor performance.
FCC is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the activation energy and is often used in oil refinery process for the rupture of high molecular weight hydrocarbon chains, a process needed to optimize the proportion of gasoline produced.
FCC particles, which are designed for a fluidized bed, are a well-known example of a composite catalyst; and the situation encountered can be considered representative