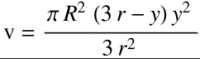Difference between revisions of "Ridwan Sholehan"
(→Study Case: Optimization Hydrogen Storage) |
(→Design Calculation of Hydrogen Storage Tank with Python Coding) |
||
| (29 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
''"Jangan Terlalu Terpaku Akan Suatu Penyesalan, Yang Terpenting Adalah Bagaimana Langkah Untuk Membangun Masa Depan Yang Lebih Baik"'' | ''"Jangan Terlalu Terpaku Akan Suatu Penyesalan, Yang Terpenting Adalah Bagaimana Langkah Untuk Membangun Masa Depan Yang Lebih Baik"'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Introduction About The Advantages of Hydrogen as a Fuel== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Hidrogen pada Kendaraan.jpg|400x400px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
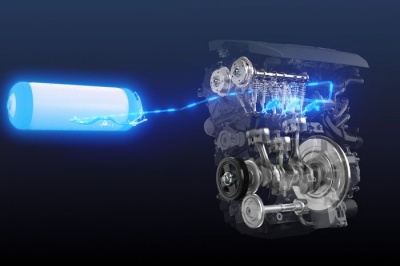
| + | Much research currently focuses on the use of hydrogen as a vehicle fuel for several reasons: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. ---Eco-Friendly--- | ||
| + | Hydrogen as a vehicle fuel produces cleaner emissions compared to fossil fuels such as gasoline and diesel. When hydrogen is burned, no carbon dioxide emissions are produced, only pure water (H2O) as a byproduct. This helps reduce the negative impact of climate change and air pollution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. ---Energy Efficiency--- | ||
| + | Hydrogen has a high energy potential and can produce more power compared to conventional fuels with a lower weight. This means vehicles that use hydrogen as fuel can have better performance and longer ranges with smaller tanks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. ---Renewable Energy Sources--- | ||
| + | Hydrogen can be produced using renewable energy sources such as solar energy and wind energy through the process of electrolysis of water. By leveraging renewable energy sources to produce hydrogen, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and accelerate the transition to clean energy. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. ---Scalable Infrastructure--- | ||
| + | One of the advantages of hydrogen is its ability to be stored and transported in large quantities. This means hydrogen can be integrated into existing infrastructure, such as existing natural gas networks or oil pipelines. This facilitates the development of hydrogen charging infrastructure for vehicles and accelerates the adoption of this technology. | ||
== Study Case: Optimization Hydrogen Storage == | == Study Case: Optimization Hydrogen Storage == | ||
| + | |||
'''Hydrogen Storage Requirement''' | '''Hydrogen Storage Requirement''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
In this case we want to build a storage with: | In this case we want to build a storage with: | ||
| + | |||
1. Capacity : 1 Liter. | 1. Capacity : 1 Liter. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 47: | ||
'''Material Classification''' | '''Material Classification''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
Hydrogen storage materials can be of different types: | Hydrogen storage materials can be of different types: | ||
| + | |||
1. dissociative material in which molecular hydrogen is dissociated into hydrogen atoms, which occupy interstitial sites. | 1. dissociative material in which molecular hydrogen is dissociated into hydrogen atoms, which occupy interstitial sites. | ||
| + | |||
2. material with chemically bound hydrogen. | 2. material with chemically bound hydrogen. | ||
| + | |||
3. materials that adsorb molecular hydrogen. | 3. materials that adsorb molecular hydrogen. | ||
Hydrogen storage in solid form can be briefly classified into the following categories: | Hydrogen storage in solid form can be briefly classified into the following categories: | ||
| + | |||
1. metal hydrides | 1. metal hydrides | ||
| + | |||
2. light metal-based hydrides | 2. light metal-based hydrides | ||
| + | |||
3. chemical hydrides (complex hydrides) | 3. chemical hydrides (complex hydrides) | ||
| + | |||
4. nanostructured materials (adsorption of molecular hydrogen) | 4. nanostructured materials (adsorption of molecular hydrogen) | ||
| Line 39: | Line 71: | ||
'''Design of Storage Tank''' | '''Design of Storage Tank''' | ||
| − | [[File:Storage Tank.png| | + | |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Storage Tank.png|400x400px|thumb|center|]] | ||
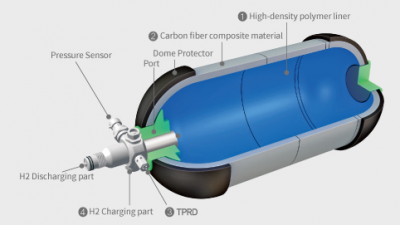
This is a reference to the design of the storage hydrogen Tank. this design has several advantages because it will be installed in a vehicle it has to be lightweight, high durability, and efficient to be used in the vehicle. | This is a reference to the design of the storage hydrogen Tank. this design has several advantages because it will be installed in a vehicle it has to be lightweight, high durability, and efficient to be used in the vehicle. | ||
'''Calculation of Hydrogen Storage''' | '''Calculation of Hydrogen Storage''' | ||
| − | [[File:Volume Storage.png| | + | |
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Volume Storage.png|400x400px|thumb|center|]] | ||
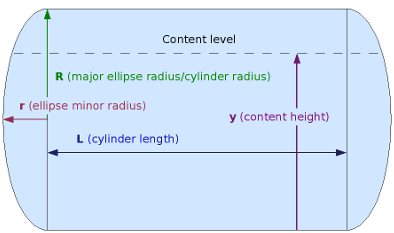
Specification: | Specification: | ||
| + | |||
1. Capacity --> Volume : 1 liter = 0.001 m^3 | 1. Capacity --> Volume : 1 liter = 0.001 m^3 | ||
2. Because this storage will be installed in vehicles, which means having limited space. we can assume for : | 2. Because this storage will be installed in vehicles, which means having limited space. we can assume for : | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | R : 10 cm = 0.1 m | |
| + | |||
| + | r : 5 cm = 0.05 m | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the bottom and top of a vertical tank, for provided values for R and r as described above, and content bisector y, with numerical ranges of 0 <= y <= r, and L+r <= y <= L+2r (with some technical adjustments of the range of y and of the resulting volume for the top ellipse): | ||
| − | + | [[File:Screenshot 2023-05-29 092048.png|200x200px|thumb|center|]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | And for the cylinder in the middle, for a provided value of R (cylinder radius) and with the numerical range of r <= y <= L+r | |
| − | [[File:Screenshot_2023-05-29_092547.png|200x200px]] | + | |
| + | [[File:Screenshot_2023-05-29_092547.png|200x200px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| − | + | So we can get L from the equation above: | |
| − | y = 0.081 m | + | |
| + | y = 0.081 m | ||
'''Tank Testing and Safety Consideration''' | '''Tank Testing and Safety Consideration''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | In accordance with ISO/TS 15869 (revised): | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Burst test: the pressure at which the tank bursts, typically more than 2× the working pressure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Proof pressure: the pressure at which the test will be executed, typically above the working pressure. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Leak test or permeation test,[9] in NmL/hr/L (Normal liter of H2/time in hr/volume of the tank.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Fatigue test, typically several thousand cycles of charging/emptying. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Bonfire test where the tank is exposed to an open fire. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 6. Bullet test where live ammunition is fired at the tank. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Design Calculation of Hydrogen Storage Tank== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1. Choose Material''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | For Material, we can use composite material such as steel aluminum, because is prepared for fabrication. This material can be easy for manufacturing processes such as cutting, shaping, or molding the material into the desired form for the tank components. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2. Spesification For Tank''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | Pressure Tank : 8 bar | ||
| + | Volume Tank : 1 liter : 0.001 m^3 | ||
| + | Budget : 500.000,- | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''3. Design Tank''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Design Tank | ||
| + | |||
| + | Assume diameter for tank is 10 cm : 0.1 m | ||
| + | |||
| + | V = πr^2h | ||
| + | 0.001 = π . (0.05^2) . h | ||
| + | h = 0.127 m or can we round it up 0.15 m | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Permissible Pressure (using safety factor) | ||
| + | |||
| + | P = 8 bar = 8 x 10^5 Pa | ||
| + | |||
| + | Permissible Pressure = 8 x 10^5 Pa x 3 = 24 x 10^5 Pa | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Standard From ASME VIII | ||
| + | |||
| + | Joint efficiency (E) : 0.85 | ||
| + | MAWS (SS-304 Seamless Pipe) : 30000 psi | ||
| + | OD : 100 mm | ||
| + | OR : 50 mm | ||
| + | Corrosion Allowance (CA) : 0.25 mm | ||
| + | Thickness (ta) : 1.27 mm | ||
| + | Thickness (t) = (ta-CA) : 1.02 mm | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Manufacturing Process | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because that shape of the material is plat, we can use manufacturing processes is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Cutting | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Bending | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. Forming | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Welding | ||
| + | |||
| + | 5. Tank Testing and Safety Consideration | ||
| + | |||
In accordance with ISO/TS 15869 (revised): | In accordance with ISO/TS 15869 (revised): | ||
| + | |||
1. Burst test: the pressure at which the tank bursts, typically more than 2× the working pressure. | 1. Burst test: the pressure at which the tank bursts, typically more than 2× the working pressure. | ||
| + | |||
2. Proof pressure: the pressure at which the test will be executed, typically above the working pressure. | 2. Proof pressure: the pressure at which the test will be executed, typically above the working pressure. | ||
| + | |||
3. Leak test or permeation test,[9] in NmL/hr/L (Normal liter of H2/time in hr/volume of the tank.) | 3. Leak test or permeation test,[9] in NmL/hr/L (Normal liter of H2/time in hr/volume of the tank.) | ||
| + | |||
4. Fatigue test, typically several thousand cycles of charging/emptying. | 4. Fatigue test, typically several thousand cycles of charging/emptying. | ||
| + | |||
5. Bonfire test where the tank is exposed to an open fire. | 5. Bonfire test where the tank is exposed to an open fire. | ||
| + | |||
6. Bullet test where live ammunition is fired at the tank. | 6. Bullet test where live ammunition is fired at the tank. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Design Calculation of Hydrogen Storage Tank with Python Coding== | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is a Final Progress to getting the design of the Hydrogen Storage Tank. in this calculation I will use a Python code: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''3D Model of Hydrogen Storage Tank:''' | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt | ||
| + | from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D | ||
| + | import numpy as np | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Input parameters | ||
| + | diameter = 0.1 # Diameter tabung dalam meter | ||
| + | length = 0.3 # Panjang tabung dalam meter | ||
| + | volume = 0.001 # Volume tabung dalam meter kubik (1 liter) | ||
| + | pressure = 8 # Tekanan tabung dalam bar | ||
| + | thickness = 0.00127 # Ketebalan plat dalam meter | ||
| + | resolution = 100 # Resolusi lingkaran permukaan tabung | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menghitung radius tabung | ||
| + | radius = diameter / 2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menghitung tinggi tabung | ||
| + | height = volume / (np.pi * radius**2) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menghasilkan koordinat titik-titik pada permukaan tabung | ||
| + | theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, resolution) | ||
| + | z = np.linspace(0, length, resolution) | ||
| + | Theta, Z = np.meshgrid(theta, z) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Koordinat penutup atas tabung (elips) | ||
| + | X_top = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta) | ||
| + | Y_top = (radius + thickness) * np.sin(Theta) | ||
| + | Z_top = np.ones_like(X_top) * length | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Koordinat penutup bawah tabung (elips) | ||
| + | X_bottom = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta) | ||
| + | Y_bottom = (radius + thickness) * np.sin(Theta) | ||
| + | Z_bottom = np.ones_like(X_bottom) * 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Koordinat permukaan tabung | ||
| + | X_cylinder = radius * np.cos(Theta) | ||
| + | Y_cylinder = radius * np.sin(Theta) | ||
| + | Z_cylinder = Z | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Membuat plot 3D | ||
| + | fig = plt.figure() | ||
| + | ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menggambar permukaan tabung | ||
| + | ax.plot_surface(X_top, Y_top, Z_top, alpha=0.5, color='grey') | ||
| + | ax.plot_surface(X_bottom, Y_bottom, Z_bottom, alpha=0.5, color='grey') | ||
| + | ax.plot_surface(X_cylinder, Y_cylinder, Z_cylinder, alpha=0.5, color='grey') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Mengatur batas sumbu x, y, dan z | ||
| + | ax.set_xlim(-(radius + thickness), (radius + thickness)) | ||
| + | ax.set_ylim(-(radius + thickness), (radius + thickness)) | ||
| + | ax.set_zlim(0, length) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Memberikan label pada sumbu x, y, dan z | ||
| + | ax.set_xlabel('X') | ||
| + | ax.set_ylabel('Y') | ||
| + | ax.set_zlabel('Z') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Memberikan judul pada plot | ||
| + | ax.set_title('Gambar 3D Tabung Silinder Kosong dengan Penutup Elips') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menampilkan plot | ||
| + | plt.show() | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is the result if we run python code above: | ||
| + | |||
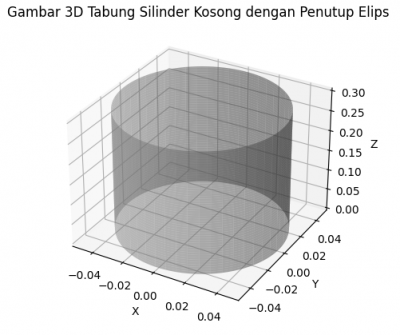
| + | [[File:Grafik_Tabung_3D_dengan_Python_Code.png|400x400px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''2D Model Front View of Hydrogen Storage Tank:''' | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt | ||
| + | import numpy as np | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Input parameters | ||
| + | diameter = 0.1 # Diameter tabung dalam meter | ||
| + | length = 0.3 # Panjang tabung dalam meter | ||
| + | thickness = 0.00127 # Ketebalan plat dalam meter | ||
| + | resolution = 100 # Resolusi lingkaran permukaan tabung | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menghitung radius tabung | ||
| + | radius = diameter / 2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menghasilkan koordinat titik-titik pada permukaan tabung | ||
| + | theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, resolution) | ||
| + | z = np.linspace(-length/2, length/2, resolution) | ||
| + | Theta, Z = np.meshgrid(theta, z) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Koordinat penutup atas tabung (elips) | ||
| + | X_top = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta) | ||
| + | Y_top = np.sqrt(((radius + thickness)**2 - (radius + thickness)**2 * (Z/length)**2)) + length/2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Koordinat penutup bawah tabung (elips) | ||
| + | X_bottom = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta) | ||
| + | Y_bottom = -np.sqrt(((radius + thickness)**2 - (radius + thickness)**2 * (Z/length)**2)) - length/2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Membuat plot 2D | ||
| + | fig, ax = plt.subplots() | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menggambar penutup atas tabung | ||
| + | ax.plot(X_top[0], Y_top[0], color='grey') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menggambar penutup bawah tabung | ||
| + | ax.plot(X_bottom[0], Y_bottom[0], color='grey') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menggambar permukaan tabung | ||
| + | ax.plot(X_top.flatten(), Y_top.flatten(), color='grey') | ||
| + | ax.plot(X_bottom.flatten(), Y_bottom.flatten(), color='grey') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Mengatur aspek rasio plot | ||
| + | ax.set_aspect('equal') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Mengatur batas sumbu x dan y | ||
| + | ax.set_xlim(-(radius + thickness), (radius + thickness)) | ||
| + | ax.set_ylim(-length/2 - thickness, length/2 + thickness) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Memberikan label pada sumbu x dan y | ||
| + | ax.set_xlabel('X') | ||
| + | ax.set_ylabel('Y') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Memberikan judul pada plot | ||
| + | ax.set_title('Tampak Depan Tabung Silinder Kosong dengan Penutup Elips') | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Menampilkan plot | ||
| + | plt.show() | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is the result if we run python code above: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Grafik_Tabung_2D_Tampak_Depan_dengan_Python_Code.png|400x400px|thumb|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Presentation Youtube''' | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | This is Link Youtube to my video in My Channel Youtube: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [https://youtube.com/watch?v=7VejH8ApECI Tugas Design Hydrogen Tank dengan menggunakan Numarical Methods - Ridwan Sholehan - 2206100312.] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:28, 12 June 2023
Contents
INTRODUCTION
Nama :Ridwan Sholehan
NPM :2206100312
Motto Hidup:
"Jangan Terlalu Terpaku Akan Suatu Penyesalan, Yang Terpenting Adalah Bagaimana Langkah Untuk Membangun Masa Depan Yang Lebih Baik"
Introduction About The Advantages of Hydrogen as a Fuel
Much research currently focuses on the use of hydrogen as a vehicle fuel for several reasons:
1. ---Eco-Friendly--- Hydrogen as a vehicle fuel produces cleaner emissions compared to fossil fuels such as gasoline and diesel. When hydrogen is burned, no carbon dioxide emissions are produced, only pure water (H2O) as a byproduct. This helps reduce the negative impact of climate change and air pollution.
2. ---Energy Efficiency--- Hydrogen has a high energy potential and can produce more power compared to conventional fuels with a lower weight. This means vehicles that use hydrogen as fuel can have better performance and longer ranges with smaller tanks.
3. ---Renewable Energy Sources--- Hydrogen can be produced using renewable energy sources such as solar energy and wind energy through the process of electrolysis of water. By leveraging renewable energy sources to produce hydrogen, we can reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and accelerate the transition to clean energy.
4. ---Scalable Infrastructure--- One of the advantages of hydrogen is its ability to be stored and transported in large quantities. This means hydrogen can be integrated into existing infrastructure, such as existing natural gas networks or oil pipelines. This facilitates the development of hydrogen charging infrastructure for vehicles and accelerates the adoption of this technology.
Study Case: Optimization Hydrogen Storage
Hydrogen Storage Requirement
In this case we want to build a storage with:
1. Capacity : 1 Liter.
2. Pressure : 8 Bar.
3. Budget : Rp. 500.000,-
4. Can be installed in a vehicle such as a motorcycle.
Material Classification
Hydrogen storage materials can be of different types:
1. dissociative material in which molecular hydrogen is dissociated into hydrogen atoms, which occupy interstitial sites.
2. material with chemically bound hydrogen.
3. materials that adsorb molecular hydrogen.
Hydrogen storage in solid form can be briefly classified into the following categories:
1. metal hydrides
2. light metal-based hydrides
3. chemical hydrides (complex hydrides)
4. nanostructured materials (adsorption of molecular hydrogen)
Refers to the type above. There is a material that can be used to build storage. Hydrogen Magnesium Hydride (MgH2) storage material by inserting a double catalyst, namely Iron Oxide (Fe2O3) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) each of 5wt% as an effort to improve the absorption properties and reaction kinetics of magnesium-based hydrogen storage materials.
Design of Storage Tank
This is a reference to the design of the storage hydrogen Tank. this design has several advantages because it will be installed in a vehicle it has to be lightweight, high durability, and efficient to be used in the vehicle.
Calculation of Hydrogen Storage
Specification:
1. Capacity --> Volume : 1 liter = 0.001 m^3
2. Because this storage will be installed in vehicles, which means having limited space. we can assume for :
R : 10 cm = 0.1 m
r : 5 cm = 0.05 m
For the bottom and top of a vertical tank, for provided values for R and r as described above, and content bisector y, with numerical ranges of 0 <= y <= r, and L+r <= y <= L+2r (with some technical adjustments of the range of y and of the resulting volume for the top ellipse):
And for the cylinder in the middle, for a provided value of R (cylinder radius) and with the numerical range of r <= y <= L+r
So we can get L from the equation above:
y = 0.081 m
Tank Testing and Safety Consideration
In accordance with ISO/TS 15869 (revised):
1. Burst test: the pressure at which the tank bursts, typically more than 2× the working pressure.
2. Proof pressure: the pressure at which the test will be executed, typically above the working pressure.
3. Leak test or permeation test,[9] in NmL/hr/L (Normal liter of H2/time in hr/volume of the tank.)
4. Fatigue test, typically several thousand cycles of charging/emptying.
5. Bonfire test where the tank is exposed to an open fire.
6. Bullet test where live ammunition is fired at the tank.
Design Calculation of Hydrogen Storage Tank
1. Choose Material
For Material, we can use composite material such as steel aluminum, because is prepared for fabrication. This material can be easy for manufacturing processes such as cutting, shaping, or molding the material into the desired form for the tank components.
2. Spesification For Tank
Pressure Tank : 8 bar Volume Tank : 1 liter : 0.001 m^3 Budget : 500.000,-
3. Design Tank
1. Design Tank
Assume diameter for tank is 10 cm : 0.1 m
V = πr^2h 0.001 = π . (0.05^2) . h h = 0.127 m or can we round it up 0.15 m
2. Permissible Pressure (using safety factor)
P = 8 bar = 8 x 10^5 Pa
Permissible Pressure = 8 x 10^5 Pa x 3 = 24 x 10^5 Pa
3. Standard From ASME VIII
Joint efficiency (E) : 0.85 MAWS (SS-304 Seamless Pipe) : 30000 psi OD : 100 mm OR : 50 mm Corrosion Allowance (CA) : 0.25 mm Thickness (ta) : 1.27 mm Thickness (t) = (ta-CA) : 1.02 mm
4. Manufacturing Process
Because that shape of the material is plat, we can use manufacturing processes is:
1. Cutting
2. Bending
3. Forming
4. Welding
5. Tank Testing and Safety Consideration
In accordance with ISO/TS 15869 (revised):
1. Burst test: the pressure at which the tank bursts, typically more than 2× the working pressure.
2. Proof pressure: the pressure at which the test will be executed, typically above the working pressure.
3. Leak test or permeation test,[9] in NmL/hr/L (Normal liter of H2/time in hr/volume of the tank.)
4. Fatigue test, typically several thousand cycles of charging/emptying.
5. Bonfire test where the tank is exposed to an open fire.
6. Bullet test where live ammunition is fired at the tank.
Design Calculation of Hydrogen Storage Tank with Python Coding
This is a Final Progress to getting the design of the Hydrogen Storage Tank. in this calculation I will use a Python code:
3D Model of Hydrogen Storage Tank:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
# Input parameters
diameter = 0.1 # Diameter tabung dalam meter
length = 0.3 # Panjang tabung dalam meter
volume = 0.001 # Volume tabung dalam meter kubik (1 liter)
pressure = 8 # Tekanan tabung dalam bar
thickness = 0.00127 # Ketebalan plat dalam meter
resolution = 100 # Resolusi lingkaran permukaan tabung
# Menghitung radius tabung
radius = diameter / 2
# Menghitung tinggi tabung
height = volume / (np.pi * radius**2)
# Menghasilkan koordinat titik-titik pada permukaan tabung
theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, resolution)
z = np.linspace(0, length, resolution)
Theta, Z = np.meshgrid(theta, z)
# Koordinat penutup atas tabung (elips)
X_top = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta)
Y_top = (radius + thickness) * np.sin(Theta)
Z_top = np.ones_like(X_top) * length
# Koordinat penutup bawah tabung (elips)
X_bottom = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta)
Y_bottom = (radius + thickness) * np.sin(Theta)
Z_bottom = np.ones_like(X_bottom) * 0
# Koordinat permukaan tabung
X_cylinder = radius * np.cos(Theta)
Y_cylinder = radius * np.sin(Theta)
Z_cylinder = Z
# Membuat plot 3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
# Menggambar permukaan tabung
ax.plot_surface(X_top, Y_top, Z_top, alpha=0.5, color='grey')
ax.plot_surface(X_bottom, Y_bottom, Z_bottom, alpha=0.5, color='grey')
ax.plot_surface(X_cylinder, Y_cylinder, Z_cylinder, alpha=0.5, color='grey')
# Mengatur batas sumbu x, y, dan z
ax.set_xlim(-(radius + thickness), (radius + thickness))
ax.set_ylim(-(radius + thickness), (radius + thickness))
ax.set_zlim(0, length)
# Memberikan label pada sumbu x, y, dan z
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
# Memberikan judul pada plot
ax.set_title('Gambar 3D Tabung Silinder Kosong dengan Penutup Elips')
# Menampilkan plot
plt.show()
This is the result if we run python code above:
2D Model Front View of Hydrogen Storage Tank:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Input parameters
diameter = 0.1 # Diameter tabung dalam meter
length = 0.3 # Panjang tabung dalam meter
thickness = 0.00127 # Ketebalan plat dalam meter
resolution = 100 # Resolusi lingkaran permukaan tabung
# Menghitung radius tabung
radius = diameter / 2
# Menghasilkan koordinat titik-titik pada permukaan tabung
theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, resolution)
z = np.linspace(-length/2, length/2, resolution)
Theta, Z = np.meshgrid(theta, z)
# Koordinat penutup atas tabung (elips)
X_top = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta)
Y_top = np.sqrt(((radius + thickness)**2 - (radius + thickness)**2 * (Z/length)**2)) + length/2
# Koordinat penutup bawah tabung (elips)
X_bottom = (radius + thickness) * np.cos(Theta)
Y_bottom = -np.sqrt(((radius + thickness)**2 - (radius + thickness)**2 * (Z/length)**2)) - length/2
# Membuat plot 2D
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Menggambar penutup atas tabung
ax.plot(X_top[0], Y_top[0], color='grey')
# Menggambar penutup bawah tabung
ax.plot(X_bottom[0], Y_bottom[0], color='grey')
# Menggambar permukaan tabung
ax.plot(X_top.flatten(), Y_top.flatten(), color='grey')
ax.plot(X_bottom.flatten(), Y_bottom.flatten(), color='grey')
# Mengatur aspek rasio plot
ax.set_aspect('equal')
# Mengatur batas sumbu x dan y
ax.set_xlim(-(radius + thickness), (radius + thickness))
ax.set_ylim(-length/2 - thickness, length/2 + thickness)
# Memberikan label pada sumbu x dan y
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
# Memberikan judul pada plot
ax.set_title('Tampak Depan Tabung Silinder Kosong dengan Penutup Elips')
# Menampilkan plot
plt.show()
This is the result if we run python code above:
Presentation Youtube
This is Link Youtube to my video in My Channel Youtube:
Tugas Design Hydrogen Tank dengan menggunakan Numarical Methods - Ridwan Sholehan - 2206100312.