Difference between revisions of "Energy Conversion System 2"
m (→3 Averaged Physical Quantities) |
m |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
2. Hefni B E, Bouskela Daniel, Modeling and Simulation of Thermal Power Plants with ThermoSysPro, Spinger, 2019 | 2. Hefni B E, Bouskela Daniel, Modeling and Simulation of Thermal Power Plants with ThermoSysPro, Spinger, 2019 | ||
| + | 3. Haar L, Gallagher J, Kell G, NBS/NRC steam tables: thermodynamic and transport | ||
| + | properties and computer program for vapor and liquid states of water in SI units. Hemisphere | ||
| + | Publishing Corporation, New York, 1975 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 4. Wagner W, Kruse A, The industrial standard IAPWS-IF97 for the thermodynamic | ||
| + | properties and other properties of water and steam. Springer, 1998 | ||
| + | |||
| + | == 2 Introduction to Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer == | ||
| + | === 2.1 What Are Thermodynamics and Thermal Hydraulics? === | ||
| + | === 2.2 Thermodynamic Processes === | ||
| + | === 2.3 Properties of Substances === | ||
| + | ==== 2.3.1 Density and Specific Volume ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.3.2 Pressure ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.3.3 Temperature ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.3.4 Energy ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.3.5 Enthalpy ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.3.6 Entropy ==== | ||
| + | === 2.4 State of a Physical System === | ||
| + | === 2.5 Selection of the State Variables === | ||
| + | === 2.6 Definition of a Thermodynamic System === | ||
| + | === 2.7 Types of Thermodynamic Systems === | ||
| + | ==== 2.7.1 Isolated System ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.7.2 Closed System ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.7.3 Open System ==== | ||
| + | === 2.8 Laws of Thermodynamics === | ||
| + | ==== 2.8.1 First Law ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.8.2 Second Law ==== | ||
| + | 2.9 Thermodynamic Cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32 | ||
| + | ==== 2.9.1 The Brayton Cycle ==== | ||
| + | ==== 2.9.2 The Rankine Cycle ==== | ||
| + | === 2.10 The Ideal Gas Law === | ||
| + | === 2.11 Polytropic Processes === | ||
| + | === 2.12 Heat Transfer Processes === | ||
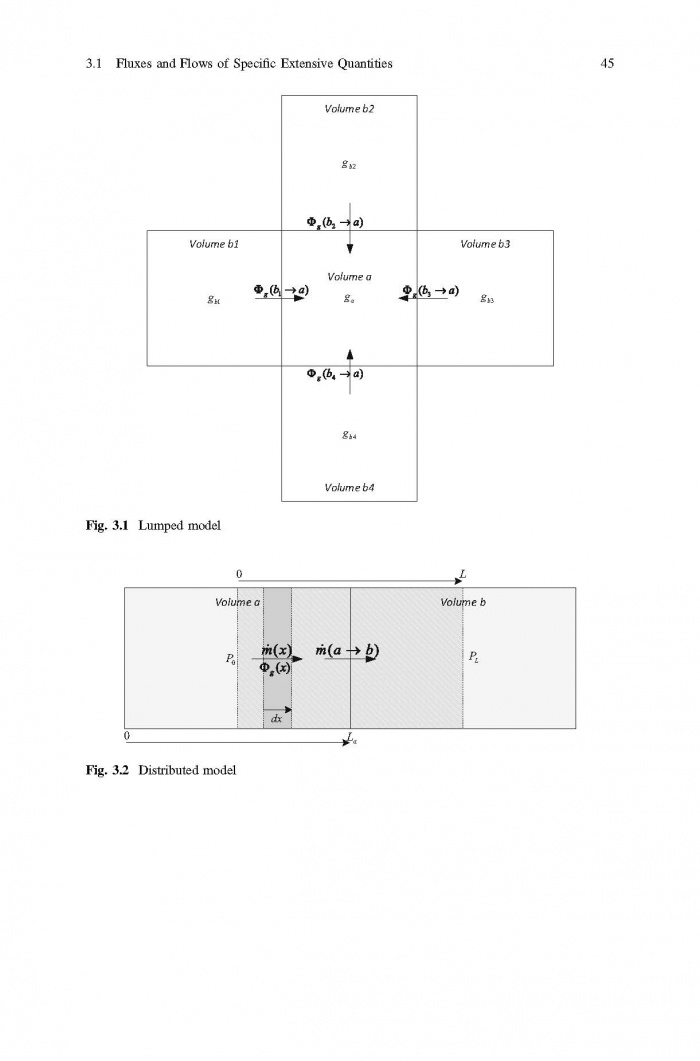
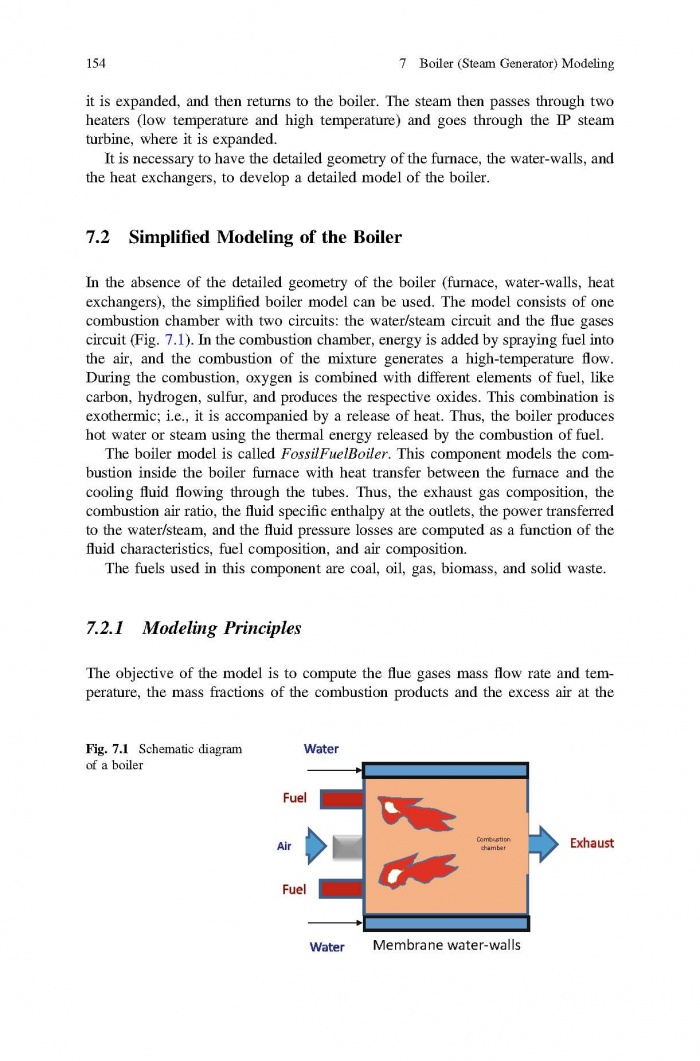
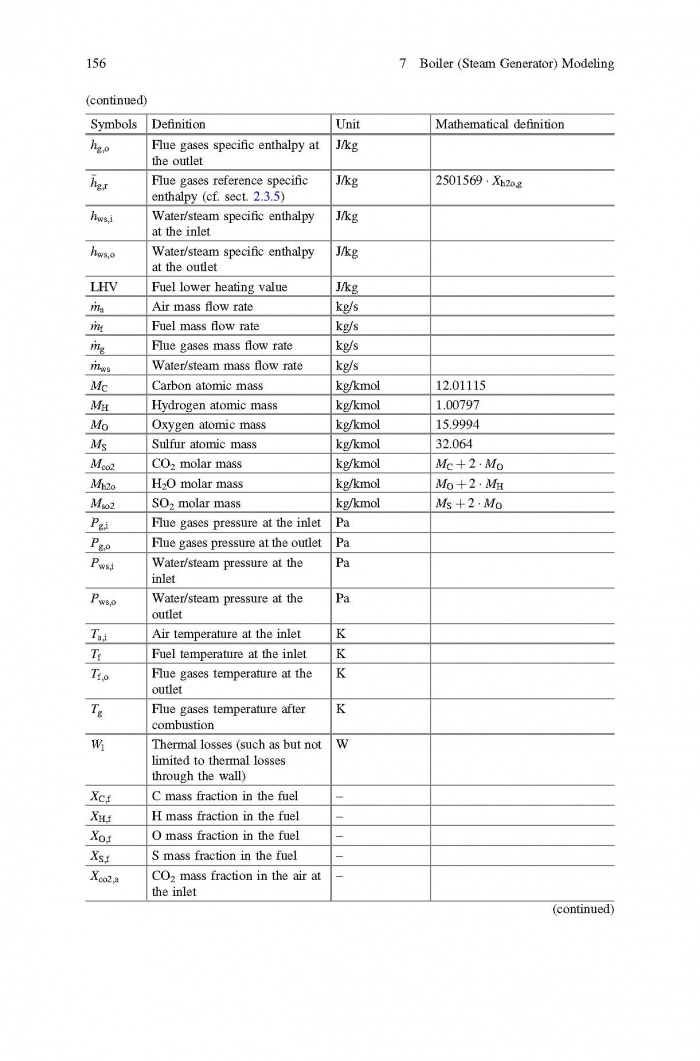
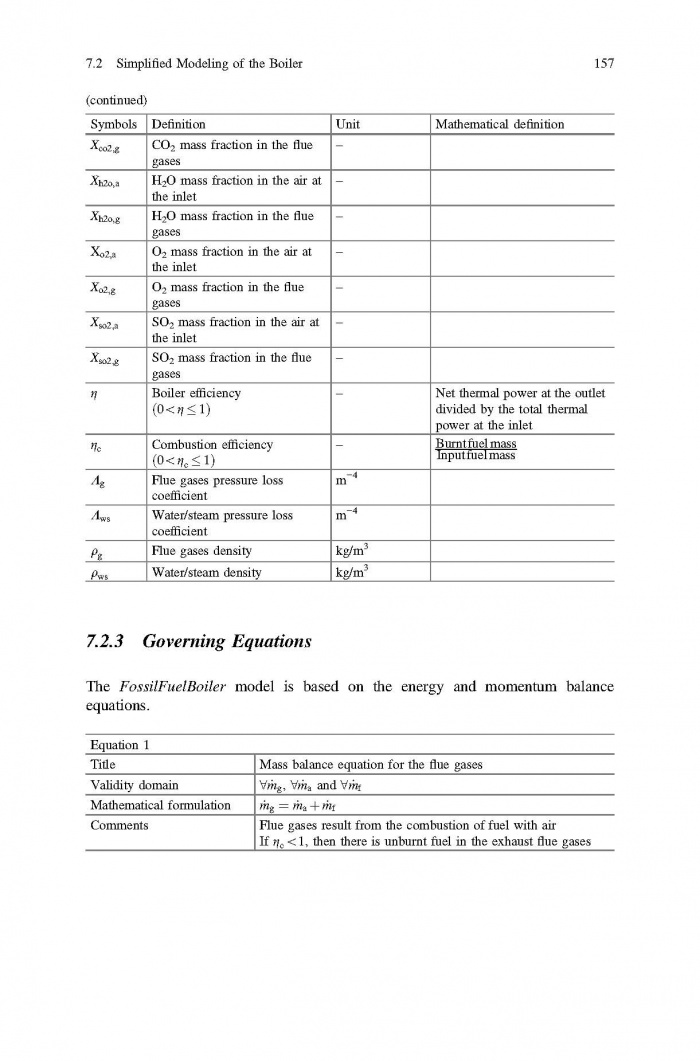
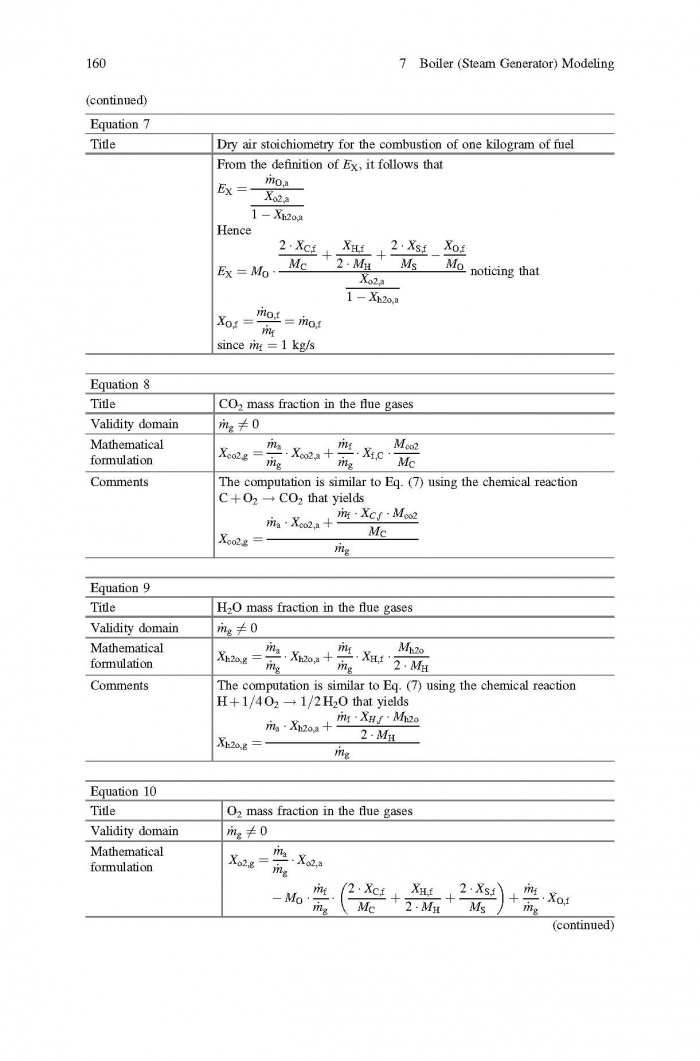
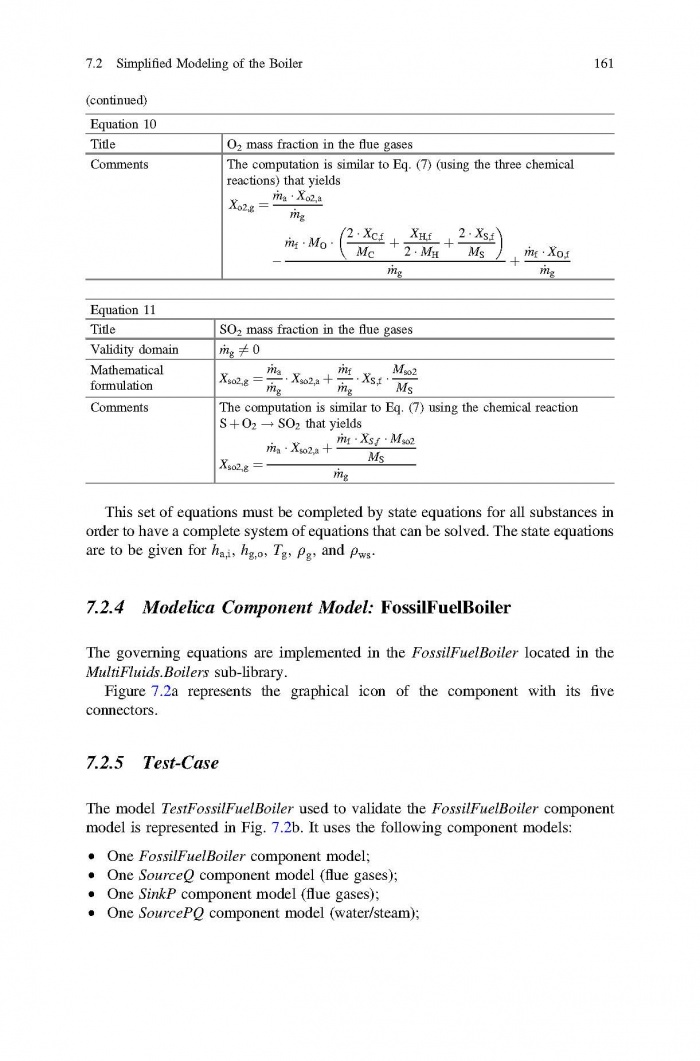
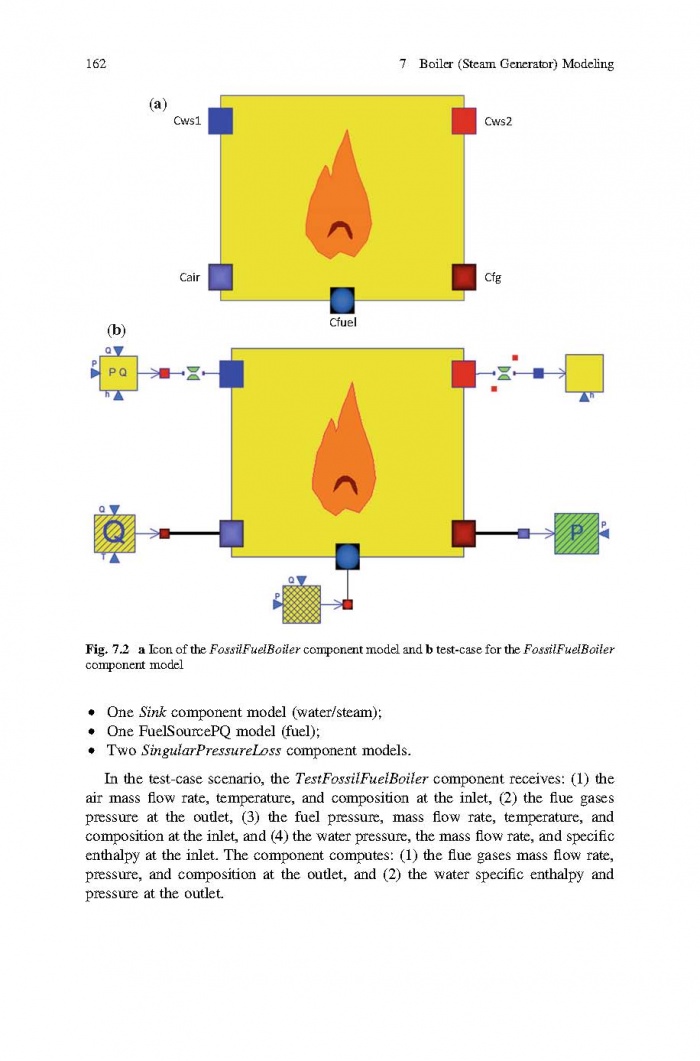
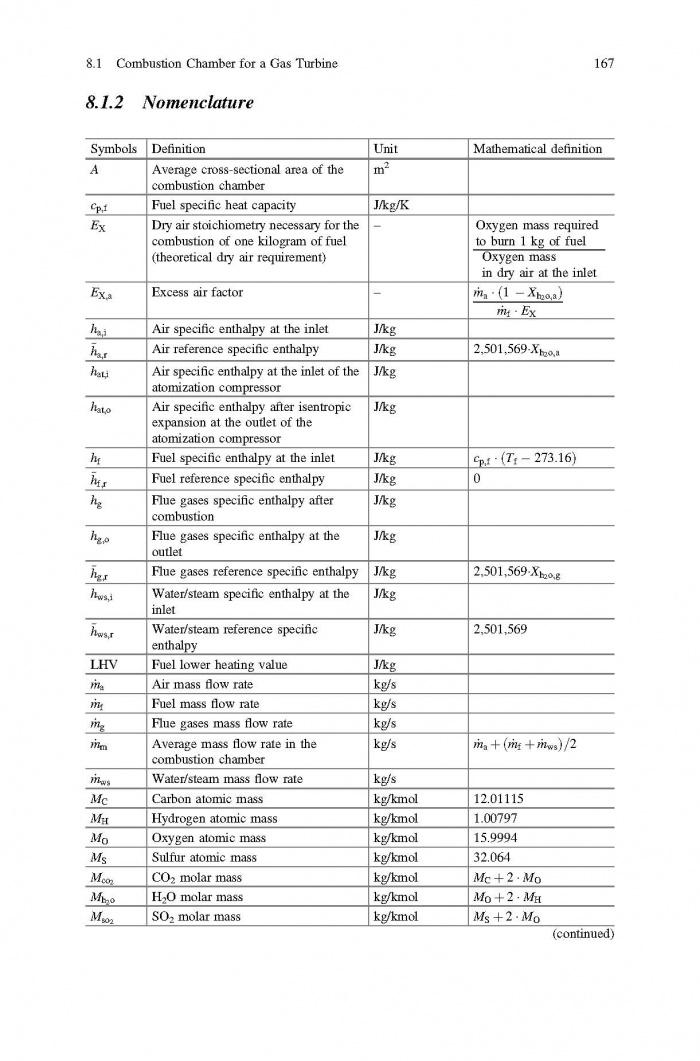
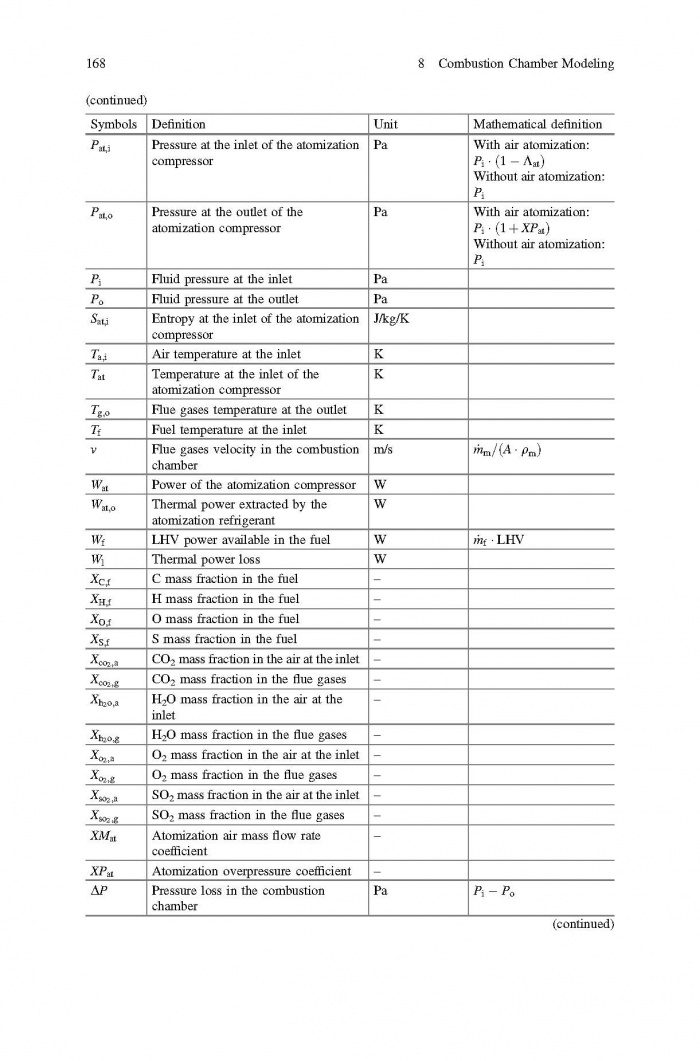
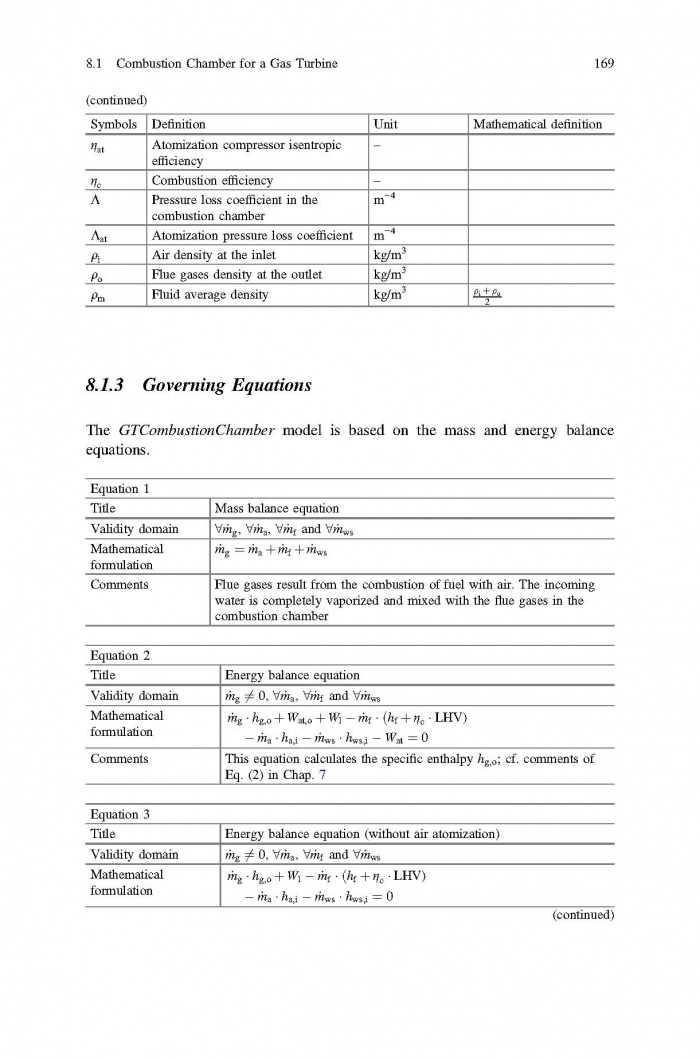
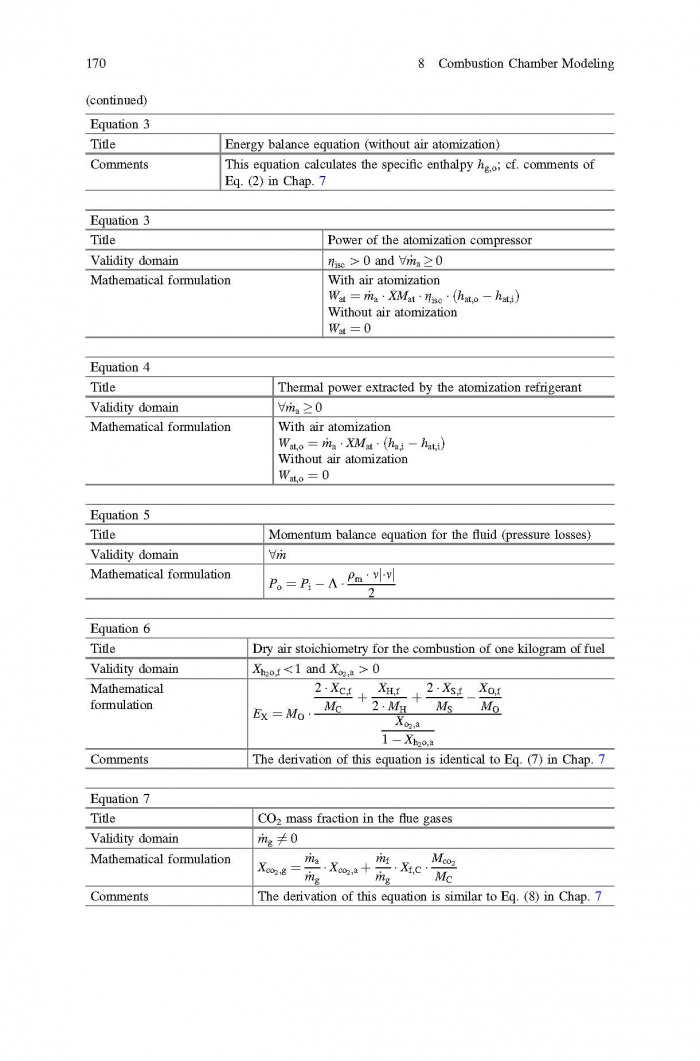
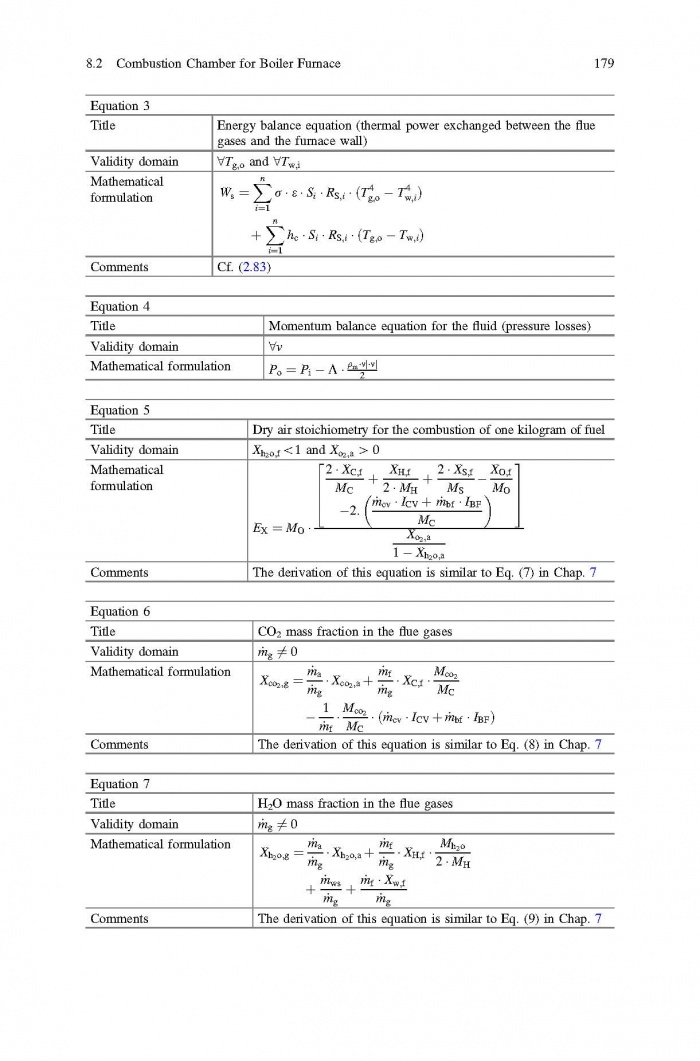
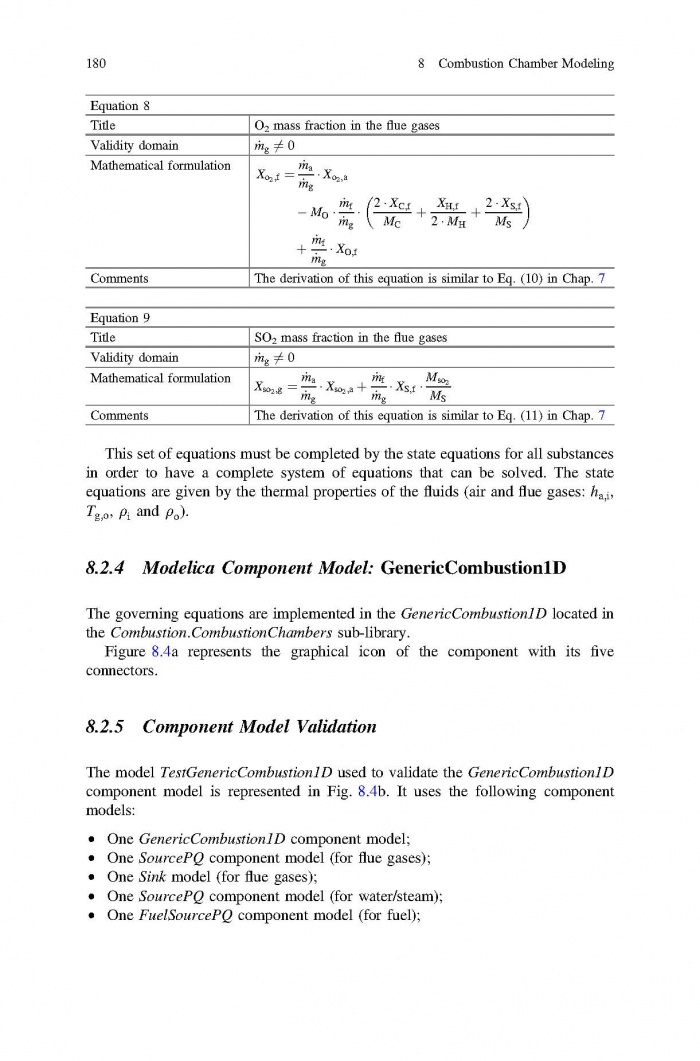
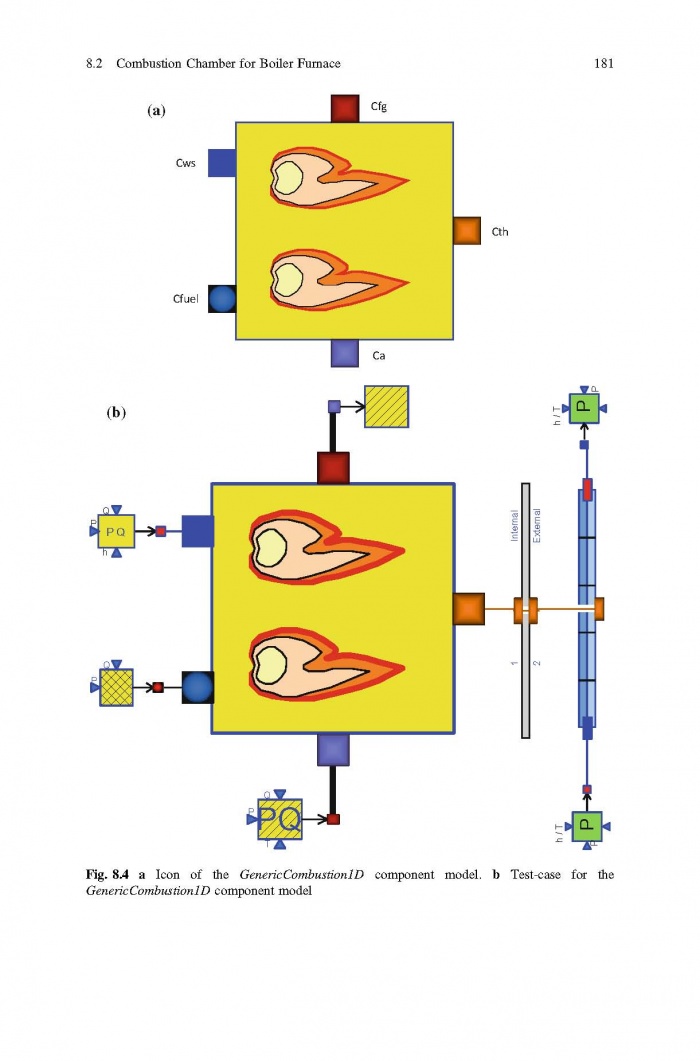
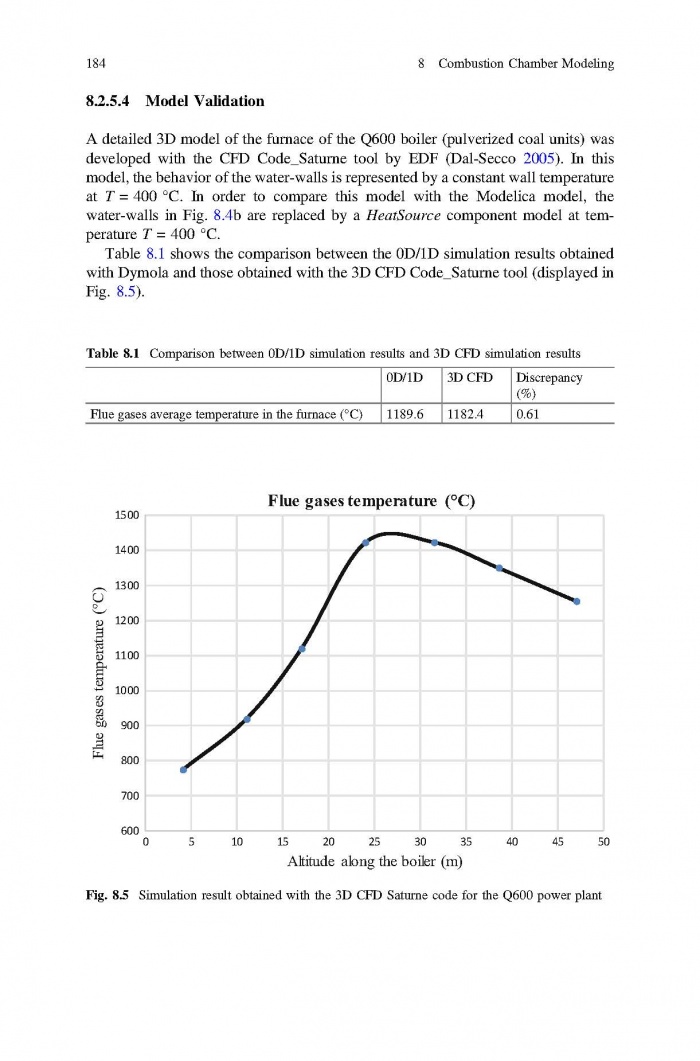
== 3 Averaged Physical Quantities == | == 3 Averaged Physical Quantities == | ||
[[File:Baligh El Hefni, Daniel Bouskela - Modeling and Simulation of Thermal Power Plants with ThermoSysPro A Theoretical Introduction and a Practical Guide-Springer International Publishing (2019) Page 060.jpg|700px]] | [[File:Baligh El Hefni, Daniel Bouskela - Modeling and Simulation of Thermal Power Plants with ThermoSysPro A Theoretical Introduction and a Practical Guide-Springer International Publishing (2019) Page 060.jpg|700px]] | ||
Revision as of 12:03, 9 March 2021
References:
1. Kreith, F, Goswami, DY, Energy Conversion (Mechanical Engineering), CNC Press, 2007
2. Hefni B E, Bouskela Daniel, Modeling and Simulation of Thermal Power Plants with ThermoSysPro, Spinger, 2019
3. Haar L, Gallagher J, Kell G, NBS/NRC steam tables: thermodynamic and transport properties and computer program for vapor and liquid states of water in SI units. Hemisphere Publishing Corporation, New York, 1975
4. Wagner W, Kruse A, The industrial standard IAPWS-IF97 for the thermodynamic properties and other properties of water and steam. Springer, 1998
Contents
- 1 2 Introduction to Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
- 1.1 2.1 What Are Thermodynamics and Thermal Hydraulics?
- 1.2 2.2 Thermodynamic Processes
- 1.3 2.3 Properties of Substances
- 1.4 2.4 State of a Physical System
- 1.5 2.5 Selection of the State Variables
- 1.6 2.6 Definition of a Thermodynamic System
- 1.7 2.7 Types of Thermodynamic Systems
- 1.8 2.8 Laws of Thermodynamics
- 1.9 2.10 The Ideal Gas Law
- 1.10 2.11 Polytropic Processes
- 1.11 2.12 Heat Transfer Processes
- 2 3 Averaged Physical Quantities
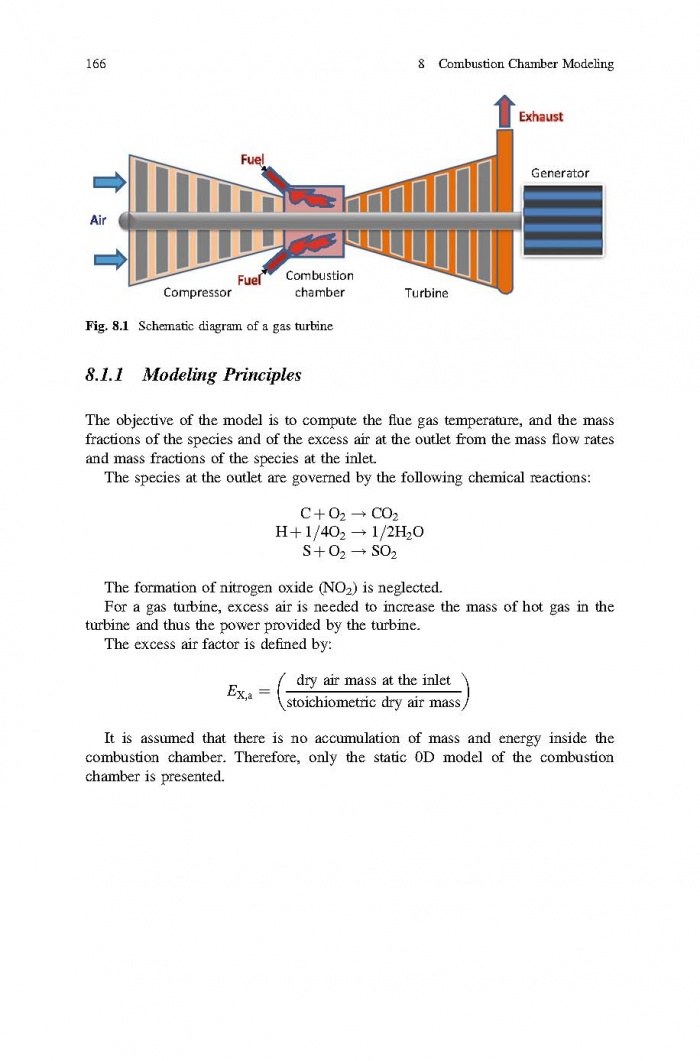
- 3 7 Boiler (Steam Generator) Modeling
- 4 8 Combustion Chamber Modeling
2 Introduction to Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer
2.1 What Are Thermodynamics and Thermal Hydraulics?
2.2 Thermodynamic Processes
2.3 Properties of Substances
2.3.1 Density and Specific Volume
2.3.2 Pressure
2.3.3 Temperature
2.3.4 Energy
2.3.5 Enthalpy
2.3.6 Entropy
2.4 State of a Physical System
2.5 Selection of the State Variables
2.6 Definition of a Thermodynamic System
2.7 Types of Thermodynamic Systems
2.7.1 Isolated System
2.7.2 Closed System
2.7.3 Open System
2.8 Laws of Thermodynamics
2.8.1 First Law
2.8.2 Second Law
2.9 Thermodynamic Cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32