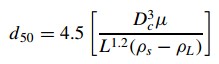Difference between revisions of "Cyclone"
Agus.nuryadi (talk | contribs) (→calculation Cyclone) |
Agus.nuryadi (talk | contribs) (→calculation Cyclone) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
Estimate the size of hydrocyclone needed to separate 90 percent of particles with a diameter greater than 20-micron m, from 10 m3/h of a dilute slurry. | Estimate the size of hydrocyclone needed to separate 90 percent of particles with a diameter greater than 20-micron m, from 10 m3/h of a dilute slurry. | ||
| + | |||
'''Physical properties:''' solid density 2000 kg/m3, liquid density 1000 kg/m3, viscosity 1 mN s/m | '''Physical properties:''' solid density 2000 kg/m3, liquid density 1000 kg/m3, viscosity 1 mN s/m | ||
Revision as of 18:23, 25 November 2020
basic calculation cyclone
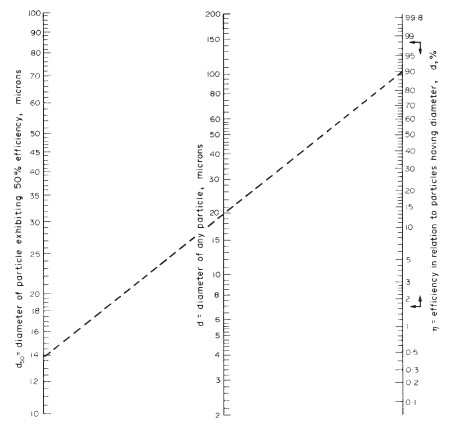
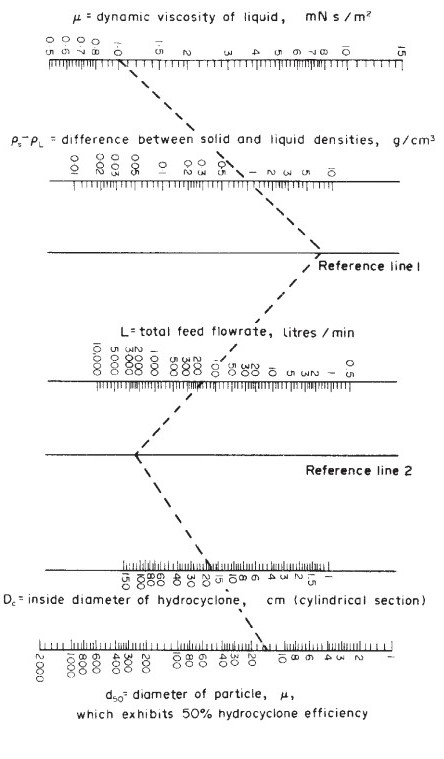
The nomographs by Zanker can be used to make a preliminary estimate of the size of cyclone needed. The specialist manufacturers of hydrocyclone equipment should be consulted to determine the best arrangements and design for a particular application. Zanker’s method is outlined below and illustrated in the Example below and based on an empirical equation by Bradley (1960):
Where:
d50 = the particle diameter for which the cyclone is 50 per cent efficient, Micron
Dc = diameter of the cyclone chamber, cm,
u = liquid viscosity, centipoise (mN s/m2),
L = feed flow rate, l/min,
pl = density of the liquid, g/cm3,
ps = density of the solid, g/cm3.
Determination of d50 from the desired particle separation
furthermore, we can see the different variable that determines cyclone such as viscosity, density, flow rate, diameter inside the cyclone.
after define Dc, we can find another dimension base on the below picture.
for calculating efficiency cyclone, we can find by below equation.
calculation Cyclone
Estimate the size of hydrocyclone needed to separate 90 percent of particles with a diameter greater than 20-micron m, from 10 m3/h of a dilute slurry.
Physical properties: solid density 2000 kg/m3, liquid density 1000 kg/m3, viscosity 1 mN s/m