Difference between revisions of "Yarynara Sebrio. S"
(→Biografi) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[File:184319526000202.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
== Biografi == | == Biografi == | ||
Nama : Yarynara Sebrio Suharyadi | Nama : Yarynara Sebrio Suharyadi | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 4 November 2019
Contents
Biografi
Nama : Yarynara Sebrio Suharyadi
SMA. : SMP-SMA Negeri Ragunan Jakarta 116 (khusus olahragawan)
TTL : Jakarta,23 September 1999
NPM : 1706070816
Jurusan : Teknik Mesin Paralel Universitas Indonesia
Hobi : Bermain Tenis lapangan
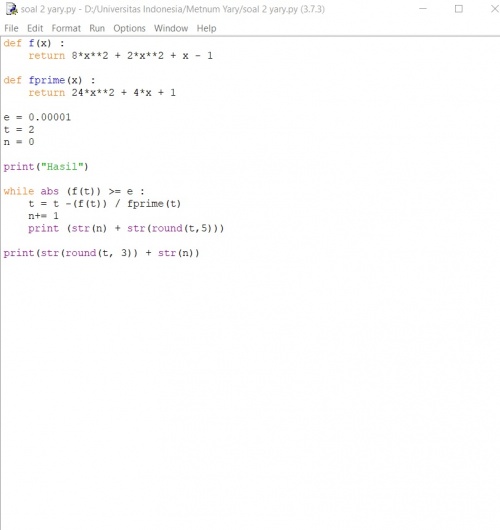
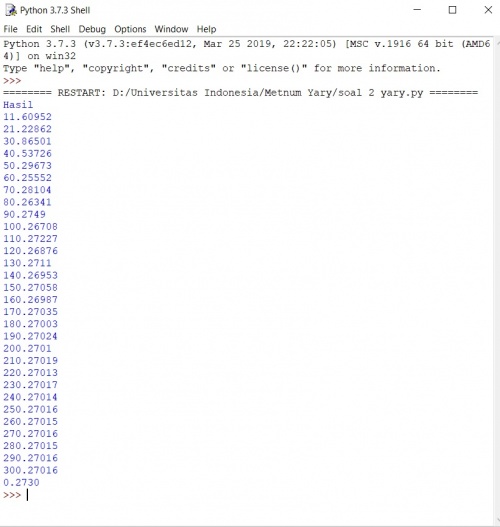
Diawal minggu belajar saya sempat kebingungan karena selalu syntax error dan tidak mengetahui caranya membuat line baru dibawah line sebelumnya. Ternyata tidak dimasukan fungsi yang benar. Hal-Hal yang sudah saya pelajari di python ini adalah mengenai operasi hitung tentang penambahan, pengurangan, pengalian, dan pembagian. Fungsi-fungsi persamaan yang sudah saya pelajari adalah a = 4
b = a + 5
print (b) 9 dan seterusnya termasuk pengalian, pengurangan dan pembagian beberapa juga ada yang mengalami kesalah pahaman seperti a = [2, 3, 4]
b = [1, 0, 3]
c = a + b print(c) [2, 1, 3, 0, 4, 3]
yang seharusnya diharapkan [3, 3, 7] ditambahlagi beberapa campuran kata dan angka akan menghasilkan eror karena tidak masuk akal dan tidak bias dilakukan operasi hitung matematika menggunakan fungsi Batasan angka seperti >, <, =, >=, dan <= memncoba program if, false, dan true dan membuat sebuah persamaan yang bias dihitung persamaan linear sederhana
Metode Numerik adalah teknik-teknik yang digunakan untuk memformulasikan masalah matematis agar dapat diselesaikan dengan operasi perhitungan. Kemampuan untuk dapat menghitung sisi segitiga (dan berarti mampu menghitung akar kuadrat) sangatlah penting, misalnya, dalam pertukangan kayu dan konstruksi. Tujuan Metode Numerik Sebelum komputer digunakan untuk penyelesaian komputasi, dilakukan dengan berbagai metode yang memiliki kendala-kendala. Seperti Metode yang digunakan antara lain: Metode Analitik, Solusi ini sangat berguna namun terbatas pada masalah sederhana. Sedangkan Masalah real yang komplek dan non linier tidak dapat diselesaikan.Metode Grafik, metode ini digunakan Sebagai pendekatan penyelesaian yang kompleks. Kendalanya bahwa metode ini Tidak akurat, sangat lama, dan banyak membutuhkan waktu. Kalkulator dan Slide Rules, Penyelesaian numerik secara manual. Cara ini cukup lama dan mungkin bisa terjadi kesalahan pemasukan data, Namun data2 tersebut tidaklah pasti selain Allah swt. Manfaat mempelajari Metode Numerik Dengan mempelajari metode numerik diharapkan mahasiswa mampu: Mampu menangani sistem persamaan besar, Ketaklinieran dan geometri yang rumit, yang dalam masalah rekayasa tidak mungkin dipecahkan secara analitis.
Tugas Metode Numerik
Video Tugas Metode Numerik
UTS
1.A import numpy as np class GEPP():
def __init__(self, A, b, doPricing=True):
#super(GEPP, self).__init__()
self.A = A # input: A is an n x n numpy matrix
self.b = b # b is an n x 1 numpy array
self.doPricing = doPricing
self.n = None # n is the length of A
self.x = None # x is the solution of Ax=b
self._validate_input() # method that validates input
self._elimination() # method that conducts elimination
self._backsub() # method that conducts back-substitution
def _validate_input(self):
self.n = len(self.A)
if self.b.size != self.n:
raise ValueError("Invalid argument: incompatible sizes between" +
"A & b.", self.b.size, self.n)
def _elimination(self):
"""
k represents the current pivot row. Since GE traverses the matrix in the
upper right triangle, we also use k for indicating the k-th diagonal
column index.
:return
"""
# Elimination
for k in range(self.n - 1):
if self.doPricing:
# Pivot
maxindex = abs(self.A[k:, k]).argmax() + k
if self.A[maxindex, k] == 0:
raise ValueError("Matrix is singular.")
# Swap
if maxindex != k:
self.Ak, maxindex = self.Amaxindex, k
self.bk, maxindex = self.bmaxindex, k
else:
if self.A[k, k] == 0:
raise ValueError("Pivot element is zero. Try setting doPricing to True.")
# Eliminate
for row in range(k + 1, self.n):
multiplier = self.A[row, k] / self.A[k, k]
self.A[row, k:] = self.A[row, k:] - multiplier * self.A[k, k:]
self.b[row] = self.b[row] - multiplier * self.b[k]
def _backsub(self):
# Back Substitution
self.x = np.zeros(self.n)
for k in range(self.n - 1, -1, -1):
self.x[k] = (self.b[k] - np.dot(self.A[k, k + 1:], self.x[k + 1:])) / self.A[k, k]
def main():
A = np.array([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[-1., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., -1., 1.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])
b = np.array([[50.],
[20.],
[5.],
[10.]])
GaussElimPiv = GEPP(np.copy(A), np.copy(b), doPricing=False)
print(GaussElimPiv.x)
print(GaussElimPiv.A)
print(GaussElimPiv.b)
GaussElimPiv = GEPP(A, b)
print(GaussElimPiv.x)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
1.B
- masukan plugin numpy
import numpy as np
def diff_y (x,y):
fungsi = x**2 - 4*y
return (fungsi)
#definisikan syarat perhitungan
x=0
y=1
h=0.7
j=5
step_size = 0.5
step_size = -np.arange (0,0.5,h)
for t in step_size:
k1 = diff_y (x,y)
k2 = diff_y ((x+0.5*h),(y+0.05*k1*h))
#simulasi hasil
w1 = y + 1/3*(k1+2*k2)
#cek kecepatan pada saat 0,7 detik
print ('maka x(0.7) sama dengan', w1)
Quiz
Quiz nomor 1.
import numpy as np
class GEPP():
def __init__(self, A, b, doPricing=True):
#super(GEPP, self).__init__()
self.A = A # input: A is an n x n numpy matrix
self.b = b # b is an n x 1 numpy array
self.doPricing = doPricing
self.n = None # n is the length of A
self.x = None # x is the solution of Ax=b
self._validate_input() # method that validates input
self._elimination() # method that conducts elimination
self._backsub() # method that conducts back-substitution
def _validate_input(self):
self.n = len(self.A)
if self.b.size != self.n:
raise ValueError("Invalid argument: incompatible sizes between" +
"A & b.", self.b.size, self.n)
def _elimination(self):
# Elimination
for k in range(self.n - 1):
if self.doPricing:
# Pivot
maxindex = abs(self.A[k:, k]).argmax() + k
if self.A[maxindex, k] == 0:
raise ValueError("Matrix is singular.")
# Swap
if maxindex != k:
self.Ak, maxindex = self.Amaxindex, k
self.bk, maxindex = self.bmaxindex, k
else:
if self.A[k, k] == 0:
raise ValueError("Pivot element is zero. Try setting doPricing to True.")
# Eliminate
for row in range(k + 1, self.n):
multiplier = self.A[row, k] / self.A[k, k]
self.A[row, k:] = self.A[row, k:] - multiplier * self.A[k, k:]
self.b[row] = self.b[row] - multiplier * self.b[k]
def _backsub(self):
# Back Substitution
self.x = np.zeros(self.n)
for k in range(self.n - 1, -1, -1):
self.x[k] = (self.b[k] - np.dot(self.A[k, k + 1:], self.x[k + 1:])) / self.A[k, k]
def main():
A = np.array([[1., 2., 0., -2., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 2., -1.],
[0., 0., 2., 1., 2.],
[0., 0., 0., -1., 1.],
[0., 1., -1., 1., -1.]])
b = np.array([[-4.],
[1.],
[1.],
[-2.],
[-1.]])
GaussElimPiv = GEPP(np.copy(A), np.copy(b), doPricing=False)
print(GaussElimPiv.x)
print(GaussElimPiv.A)
print(GaussElimPiv.b)
GaussElimPiv = GEPP(A, b)
print(GaussElimPiv.x)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Quiz no.2
import numpy as np
def diff_y (x,y):
fungsi = x**2 - 4*y
returm (fungsi)
x=0
y=1
h=0,01
step_size=np.arrange (0,0,03,h)
for t in step_size:
k1=diff_y (x,y)
k2=diff_y ((x+0.5*h), (y+0,5*kl*h))
y=y+kl*h
print ('make y(0.03) adalah ',y)
Tugas 1
x1 = 0
dx1 = ('0.1')
dx = float (dx1)
x2 = x1+dx
Fx_1 = ((x2**2)-1) / (x1-1)
n = 1 error = 0
print ("n x F(x) error")
print (n," ",x1," ",Fx_1," ",error)
while x2<1 :
Fx_2 = ((x2**2)-1) / (x2-1)
error = ((Fx_2-Fx_1) / Fx_1)
Fx_1 = Fx_2
n = n+1
print (n," ",x1," ",Fx_1," ",error)
x2=x2+dx
Tugas 2
Tugas 3
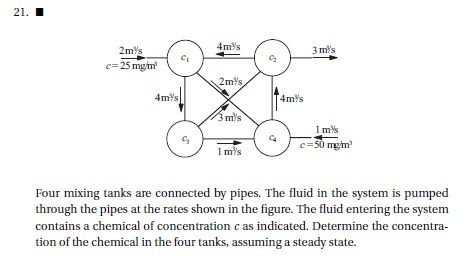
Soal ini dikerjakan dengan menggunakan Hukum Kontinuitas Massa Definisi : massa yang masuk ke dalam sistem akan sama dengan massa yang keluar dari sistem
Rumus Q*p=Q*p
Karena terdapat 4 variabel, maka terdapat 4 persamaan
6C1 - 4C2 = 50
-2C1 - 1C3 + 4C4 = 50
7C2 - 3C3 - 4C4 = 0
-4C1 + 4C3 = 0
6C1 - 4C2 + 0C3 + 0C4 = 50
-2C1 + 0C2 - 1C3 + 4C4 = 50
0C1 + 7C2 - 3C3 - 4C4 = 0
-4C1 + 0C2 + 4C3 + 0C4 = 0
Dari model python akan didapatkan nilai
C1 = 275/9
C2 = 100/3
C3 = 275/9
C4 = 425/12
- python segera menyusul